Resurrection of vitamin D deficiency and rickets
- PMID: 16886050
- PMCID: PMC1523417
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI29449
Resurrection of vitamin D deficiency and rickets
Abstract
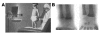
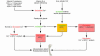
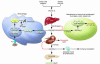
The epidemic scourge of rickets in the 19th century was caused by vitamin D deficiency due to inadequate sun exposure and resulted in growth retardation, muscle weakness, skeletal deformities, hypocalcemia, tetany, and seizures. The encouragement of sensible sun exposure and the fortification of milk with vitamin D resulted in almost complete eradication of the disease. Vitamin D (where D represents D2 or D3) is biologically inert and metabolized in the liver to 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D], the major circulating form of vitamin D that is used to determine vitamin D status. 25(OH)D is activated in the kidneys to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D], which regulates calcium, phosphorus, and bone metabolism. Vitamin D deficiency has again become an epidemic in children, and rickets has become a global health issue. In addition to vitamin D deficiency, calcium deficiency and acquired and inherited disorders of vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus metabolism cause rickets. This review summarizes the role of vitamin D in the prevention of rickets and its importance in the overall health and welfare of infants and children.
Figures


References
-
- Holick, M.F. 2005. Vitamin D. InModern nutrition in health and disease. 10th edition. M. Shils et al., editors. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Baltimore, Maryland, USA. 329–345.
-
- Rajakumar K. Vitamin D, cod-liver oil, sunlight, and rickets: a historical perspective. Pediatrics. . 2003;112:132–135. - PubMed
-
- Mozolowski W. Jedrzej Sniadecki (1768–1838) on the cure of rickets. Nature. . 1939;143:121–124.
-
- Palm T.A. The geographical distribution and etiology of rickets. Practitioner. . 1890;45:270–342.
-
- Huldschinsky K. Heilung von Rachitis durch künstliche Höhensonne. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. . 1919;45:712–713.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

