Autophagy is involved in T cell death after binding of HIV-1 envelope proteins to CXCR4
- PMID: 16886061
- PMCID: PMC1523410
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI26185
Autophagy is involved in T cell death after binding of HIV-1 envelope proteins to CXCR4
Abstract
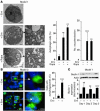
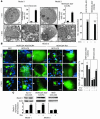
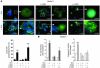
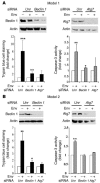
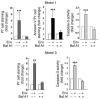
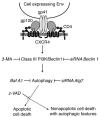
HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins (Env), expressed at the cell surface, induce apoptosis of uninfected CD4+ T cells, contributing to the development of AIDS. Here we demonstrate that, independently of HIV replication, transfected or HIV-infected cells that express Env induced autophagy and accumulation of Beclin 1 in uninfected CD4+ T lymphocytes via CXCR4. The same phenomena occurred in a T cell line and in transfected HEK.293 cells that expressed both wild-type CXCR4 and a truncated form of CD4 that is unable to bind the lymphocyte-specific protein kinase Lck. Env-mediated autophagy is required to trigger CD4+ T cell apoptosis since blockade of autophagy at different steps, by either drugs (3-methyladenine and bafilomycin A1) or siRNAs specific for Beclin 1/Atg6 and Atg7 genes, totally inhibited the apoptotic process. Furthermore, CD4+ T cells still underwent Env-mediated cell death with autophagic features when apoptosis was inhibited. These results suggest that HIV-infected cells can induce autophagy in bystander CD4+ T lymphocytes through contact of Env with CXCR4, leading to apoptotic cell death, a mechanism most likely contributing to immunodeficiency.
Figures

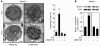

Comment in
-
HIV and CXCR4 in a kiss of autophagic death.J Clin Invest. 2006 Aug;116(8):2078-80. doi: 10.1172/JCI29447. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16886053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corbeil J., Richman D.D. Productive infection and subsequent interaction of CD4-gp120 at the cellular membrane is required for HIV-induced apoptosis of CD4+ T cells. . J. Gen. Virol. 1995;76:681–690. - PubMed
-
- Laurent-Crawford A.G., et al. Membrane expression of HIV envelope glycoproteins triggers apoptosis in CD4 cells. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses. 1993;9:761–773. - PubMed
-
- Garcia E., et al. HIV-1 trafficking to the dendritic cell-T-cell infectious synapse uses a pathway of tetraspanin sorting to the immunological synapse. . Traffic. 2005;6:488–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

