Generation of a large scale repertoire of Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) from normalised rainbow trout cDNA libraries
- PMID: 16887034
- PMCID: PMC1564016
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-196
Generation of a large scale repertoire of Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) from normalised rainbow trout cDNA libraries
Abstract
Background: Within the framework of a genomics project on livestock species (AGENAE), we initiated a high-throughput DNA sequencing program of Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss.
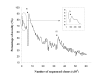
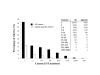
Results: We constructed three cDNA libraries including one highly complex pooled-tissue library. These libraries were normalized and subtracted to reduce clone redundancy. ESTs sequences were produced, and 96,472 ESTs corresponding to high quality sequence reads were released on the international database, currently representing 42.5% of the overall sequence knowledge in this species. All these EST sequences and other publicly available ESTs in rainbow trout have been included on a publicly available Website (SIGENAE) and have been clustered into a total of 52,930 clusters of putative transcripts groups, including 24,616 singletons. 57.1% of these 52,930 clusters are represented by at least one Agenae EST and 14,343 clusters (27.1%) are only composed by Agenae ESTs. Sequence analysis also reveals that normalization and especially subtraction were effective in decreasing redundancy, and that the pooled-tissue library was representative of the initial tissue complexity.
Conclusion: Due to present work on the construction of rainbow trout normalized cDNA libraries and their extensive sequencing, along with other large scale sequencing programs, rainbow trout is now one of the major fish models in term of EST sequences available in a public database, just after Zebrafish, Danio rerio. This information is now used for the selection of a non redundant set of clones for producing DNA micro-arrays in order to examine global gene expression.
Figures

References
-
- Thorgaard GH, Bailey GS, Williams D, Buhler DR, Kaattari SL, Ristow SS, Hansen JD, Winton JR, Bartholomew JL, Nagler JJ, Walsh PJ, Vijayan MM, Devlin RH, Hardy RW, Overturf KE, Young WP, Robison BD, Rexroad C, Palti Y. Status and opportunities for genomics research with rainbow trout. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;133:609–46. doi: 10.1016/S1096-4959(02)00167-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rise ML, von Schalburg KR, Brown GD, Mawer MA, Devlin RH, Kuipers N, Busby M, Beetz-Sargent M, Alberto R, Gibbs AR, Hunt P, Shukin R, Zeznik JA, Nelson C, Jones SR, Smailus DE, Jones SJ, Schein JE, Marra MA, Butterfield YS, Stott JM, Ng SH, Davidson WS, Koop BF. Development and application of a salmonid EST database and cDNA microarray: data mining and interspecific hybridization characteristics. Genome Res. 2004;14:478–90. doi: 10.1101/gr.1687304. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- AGENAE http://www.inra.fr/agenae/
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

