Identification and characterization of a human monoclonal antagonistic antibody AL-57 that preferentially binds the high-affinity form of lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1
- PMID: 16888085
- PMCID: PMC1712386
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.1105649
Identification and characterization of a human monoclonal antagonistic antibody AL-57 that preferentially binds the high-affinity form of lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1
Abstract
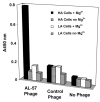
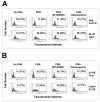
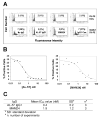
LFA-1 (alpha(L)beta(2)) mediates cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix adhesions essential for immune and inflammatory responses. One critical mechanism regulating LFA-1 activity is the conformational change of the ligand-binding alpha(L) I domain from low-affinity (LA), closed form, to the high-affinity (HA), open form. Most known integrin antagonists bind both forms. Antagonists specific for the HA alpha(L) I domain have not been described. Here, we report the identification and characterization of a human antibody AL-57, which binds to the alpha(L) I domain in a HA but not LA conformation. AL-57 was discovered by selection from a human Fab-displaying library using a locked-open HA I domain as target. AL-57 Fab-phage bound HA I domain-expressing K562 cells (HA cells) in a Mg(2+)-dependent manner. AL-57 IgG also bound HA cells and PBMCs, activated by Mg(2+)/EGTA, PMA, or DTT. The binding profile of AL-57 IgG on PBMCs was the same as that of ICAM-1, the main ligand of LFA-1. In contrast, an anti-alpha(L) murine mAb MHM24 did not distinguish between the HA and LA forms. Moreover, AL-57 IgG blocked ICAM-1 binding to HA cells with a potency greater than MHM24. It also inhibited ICAM-1 binding to PBMCs, blocked adhesion of HA cells to keratinocytes, and inhibited PHA-induced lymphocyte proliferation with potencies comparable with MHM24. These results indicate that specifically targeting the HA I domain is sufficient to inhibit LFA-1-mediated, adhesive functions. AL-57 represents a therapeutic candidate for treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Figures




References
-
- Shimaoka M, Takagi J, Springer TA. Conformational regulation of integrin structure and function. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2002;31:485–516. - PubMed
-
- Springer TA. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990;346:425–434. - PubMed
-
- Carman CV, Jun C, Salas A, Springer TA. Endothelial cells proactively form microvilli-like membrane projections upon intercellular adhesion molecule 1 engagement of leukocyte LFA-1. J Immunol. 2003;171:6135–6144. - PubMed
-
- Larson RS, Springer TA. Structure and function of leukocyte integrins. Immunol Rev. 1990;114:181–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

