Recent advances in intravesical drug/gene delivery
- PMID: 16889430
- PMCID: PMC2504416
- DOI: 10.1021/mp060001j
Recent advances in intravesical drug/gene delivery
Abstract
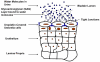
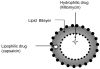
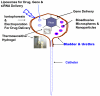
Targeting of drugs administered systemically relies on the higher affinity of ligands for specific receptors to obtain selectivity in drug response. However, achieving the same goal inside the bladder is much easier with an intelligent pharmaceutical approach that restricts drug effects by exploiting the pelvic anatomical architecture of the human body. This regional therapy involves placement of drugs directly into the bladder through a urethral catheter. It is obvious that drug administration by this route holds advantage in chemotherapy of superficial bladder cancer, and it has now become the most widely used treatment modality for this ailment. In recent years, the intravesical route has also been exploited either as an adjunct to an oral regimen or as a second-line treatment for neurogenic bladder. (Lamm, D. L.; Griffith, J. G. Semin. Urol. 1992, 10, 39-44. Igawa, Y.; Satoh, T.; Mizusawa, H.; Seki, S.; Kato, H.; Ishizuka, O.; Nishizawa, O. BJU Int. 2003, 91, 637-641.) Instillation of DNA via this route using different vectors has been able to restrict the transgene expression in organs other than bladder. The present review article will discuss the shortcomings of the current options available for intravesical drug delivery (IDD) and lay a perspective for future developments in this field.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Local drug delivery to bladder using technology innovations.Urol Clin North Am. 2006 Nov;33(4):519-30, x. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2006.06.012. Urol Clin North Am. 2006. PMID: 17011388 Review.
-
Intravesical drug delivery: Challenges, current status, opportunities and novel strategies.J Control Release. 2010 Dec 1;148(2):147-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.08.031. Epub 2010 Sep 8. J Control Release. 2010. PMID: 20831887 Review.
-
Intravesical drug delivery for dysfunctional bladder.Int J Urol. 2013 Jun;20(6):552-62. doi: 10.1111/iju.12085. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Int J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23336527
-
Innovative applications of natural polysaccharide polymers in intravesical therapy of bladder diseases.Carbohydr Polym. 2025 Apr 15;354:123307. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2025.123307. Epub 2025 Jan 22. Carbohydr Polym. 2025. PMID: 39978897 Review.
-
Intravesical liposome therapy for interstitial cystitis.Int J Urol. 2017 Apr;24(4):262-271. doi: 10.1111/iju.13317. Epub 2017 Mar 4. Int J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28258657 Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced Peptide Nanomedicines for Bladder Cancer Theranostics.Front Chem. 2022 Aug 5;10:946865. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.946865. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 35991612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel targeted bladder drug-delivery systems: a review.Res Rep Urol. 2015 Nov 23;7:169-78. doi: 10.2147/RRU.S56168. eCollection 2015. Res Rep Urol. 2015. PMID: 26649286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revitalizing Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer: Nanotechnology and Bioengineering Approaches.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 15;16(8):1067. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081067. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotechnology as a tool to advance research and treatment of non-oncologic urogenital diseases.Ther Adv Urol. 2022 Jul 26;14:17562872221109023. doi: 10.1177/17562872221109023. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Urol. 2022. PMID: 35924206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intravesical instillation of pentosan polysulfate encapsulated in a liposome nanocarrier for interstitial cystitis.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2014 Jul 12;2(2):145-8. eCollection 2014. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2014. PMID: 25374916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lamm DL, Griffith JG. Semin Urol. 1992;10:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Igawa Y, Satoh T, Mizusawa H, Seki S, Kato H, Ishizuka O, Nishizawa O. BJU Int. 2003;91:637–641. - PubMed
-
- Buyse G, Waldeck K, Verpoorten C, Bjork H, Casaer P, Andersson KE. J Urol. 1998;160:892–896. - PubMed
-
- Kelly JD, Young MR, Johnston SR, Keane PF. Eur Urol. 1998;34:53–56. - PubMed
-
- Gao X, Au JL, Badalament RA, Wientjes MG. Clin Cancer Res. 1998;4:139–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

