Molecular dipstick test for diagnosis of sleeping sickness
- PMID: 16891507
- PMCID: PMC1594664
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02594-05
Molecular dipstick test for diagnosis of sleeping sickness
Abstract
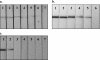
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) or sleeping sickness is a neglected disease that affects poor rural populations across sub-Saharan Africa. Confirmation of diagnosis is based on detection of parasites in either blood or lymph by microscopy. Here we present the development and the first-phase evaluation of a simple and rapid test (HAT-PCR-OC [human African trypanosomiasis-PCR-oligochromatography]) for detection of amplified Trypanosoma brucei DNA. PCR products are visualized on a dipstick through hybridization with a gold-conjugated probe (oligochromatography). Visualization is straightforward and takes only 5 min. Controls both for the PCR and for DNA migration are incorporated into the assay. The lower detection limit of the test is 5 fg of pure T. brucei DNA. One parasite in 180 microl of blood is still detectable. Sensitivity and specificity for T. brucei were calculated at 100% when tested on blood samples from 26 confirmed sleeping sickness patients, 18 negative controls (nonendemic region), and 50 negative control blood samples from an endemic region. HAT-PCR-OC is a promising new tool for diagnosis of sleeping sickness in laboratory settings, and the diagnostic format described here may have wider application for other infectious diseases.
Figures



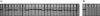
References
-
- Anonymous. 2006. Human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness): epidemiological update. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 81:69-80. - PubMed
-
- Becker, S., J. R. Franco, P. P. Simarro, A. Stich, P. M. Abel, and D. Steverding. 2004. Real-time PCR for detection of Trypanosoma brucei in human blood samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 50:193-199. - PubMed
-
- Chang, A. B., and J. D. Fox. 1999. NASBA and other transcription based amplification methods for research and diagnostic microbiology. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 10:185-196.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

