Smc5-Smc6 mediate DNA double-strand-break repair by promoting sister-chromatid recombination
- PMID: 16892052
- PMCID: PMC4493748
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1466
Smc5-Smc6 mediate DNA double-strand-break repair by promoting sister-chromatid recombination
Abstract
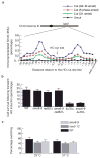
DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) can arise during DNA replication, or after exposure to DNA-damaging agents, and their correct repair is fundamental for cell survival and genomic stability. Here, we show that the Smc5-Smc6 complex is recruited to DSBs de novo to support their repair by homologous recombination between sister chromatids. In addition, we demonstrate that Smc5-Smc6 is necessary to suppress gross chromosomal rearrangements. Our findings show that the Smc5-Smc6 complex is essential for genome stability as it promotes repair of DSBs by error-free sister-chromatid recombination (SCR), thereby suppressing inappropriate non-sister recombination events.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

