TBLR1 regulates the expression of nuclear hormone receptor co-repressors
- PMID: 16893456
- PMCID: PMC1555579
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-7-31
TBLR1 regulates the expression of nuclear hormone receptor co-repressors
Abstract
Background: Transcription is regulated by a complex interaction of activators and repressors. The effectors of repression are large multimeric complexes which contain both the repressor proteins that bind to transcription factors and a number of co-repressors that actually mediate transcriptional silencing either by inhibiting the basal transcription machinery or by recruiting chromatin-modifying enzymes.
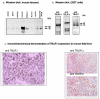
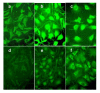
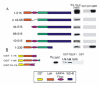
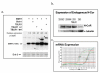
Results: TBLR1 [GenBank: NM024665] is a co-repressor of nuclear hormone transcription factors. A single highly conserved gene encodes a small family of protein molecules. Different isoforms are produced by differential exon utilization. Although the ORF of the predominant form contains only 1545 bp, the human gene occupies approximately 200 kb of genomic DNA on chromosome 3q and contains 16 exons. The genomic sequence overlaps with the putative DC42 [GenBank: NM030921] locus. The murine homologue is structurally similar and is also located on Chromosome 3. TBLR1 is closely related (79% homology at the mRNA level) to TBL1X and TBL1Y, which are located on Chromosomes X and Y. The expression of TBLR1 overlaps but is distinct from that of TBL1. An alternatively spliced form of TBLR1 has been demonstrated in human material and it too has an unique pattern of expression. TBLR1 and the homologous genes interact with proteins that regulate the nuclear hormone receptor family of transcription factors. In resting cells TBLR1 is primarily cytoplasmic but after perturbation the protein translocates to the nucleus. TBLR1 co-precipitates with SMRT, a co-repressor of nuclear hormone receptors, and co-precipitates in complexes immunoprecipitated by antiserum to HDAC3. Cells engineered to over express either TBLR1 or N- and C-terminal deletion variants, have elevated levels of endogenous N-CoR. Co-transfection of TBLR1 and SMRT results in increased expression of SMRT. This co-repressor undergoes ubiquitin-mediated degradation and we suggest that the stabilization of the co-repressors by TBLR1 occurs because of a novel mechanism that protects them from degradation. Transient over expression of TBLR1 produces growth arrest.
Conclusion: TBLR1 is a multifunctional co-repressor of transcription. The structure of this family of molecules is highly conserved and closely related co-repressors have been found in all eukaryotic organisms. Regulation of co-repressor expression and the consequent alterations in transcriptional silencing play an important role in the regulation of differentiation.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

