Muscarinic receptor-activated cationic channels in murine ileal myocytes
- PMID: 16894345
- PMCID: PMC2013797
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706852
Muscarinic receptor-activated cationic channels in murine ileal myocytes
Abstract
Background and purpose: There is little information about the excitatory cholinergic mechanisms of mouse small intestine although this model is important for gene knock-out studies.
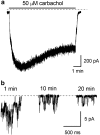
Experimental approach: Using patch-clamp techniques, voltage-dependent and pharmacological properties of carbachol- or intracellular GTPgammaS-activated cationic channels in mouse ileal myocytes were investigated.
Key results: Three types of cation channels were identified in outside-out patches (17, 70 and 140 pS). The voltage-dependent behaviour of the 70 pS channel, which was also the most abundantly expressed channel (approximately 0.35 micro(-2)) was most consistent with the properties of the whole-cell muscarinic current (half-maximal activation at -72.3+/-9.3 mV, slope of -9.1+/-7.4 mV and mean open probability of 0.16+/-0.01 at -40 mV; at near maximal activation by 50 microM carbachol). Both channel conductance and open probability depended on the permeant cation in the order: Cs+ (70 pS) >Rb+ (66pS) >Na+ (47 pS) >Li+ (30 pS). External application of divalent cations, quinine, SK&F 96365 or La3+ strongly inhibited the whole-cell current. At the single channel level the nature of the inhibitory effects appeared to be very different. Either reduction of the open probability (quinine and to some extent SK&F 96365 and La3+) or of unitary current amplitude (Ca2+, Mg2+, SK&F 96365, La3+) was observed implying significant differences in the dissociation rates of the blockers.
Conclusions and implications: The muscarinic cation current of murine small intestine is very similar to that in guinea-pig myocytes and murine genetic manipulation should yield important information about muscarinic receptor transduction mechanisms.
Published online 7 August 2006.
Figures





References
-
- Ahn SC, Kim SJ, So I, Kim KW. Inhibitory effect of phorbol 12,13 dibutyrate on carbachol-activated nonselective cationic current in guinea-pig gastric myocytes. Pflugers Arch. 1997;434:505–507. - PubMed
-
- Bolton TB, Zholos AV. Activation of M2 muscarinic receptors in guinea-pig ileum opens cationic channels modulated by M3 muscarinic receptors. Life Sci. 1997;60:1121–1128. - PubMed
-
- Boulay G, Zhu X, Peyton M, Jiang M, Hurst R, Stefani E, et al. Cloning and expression of a novel mammalian homolog of Drosophila transient receptor potential (Trp) involved in calcium entry secondary to activation of receptors coupled by the Gq class of G protein. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29672–29680. - PubMed
-
- Bymaster FP, Carter PA, Zhang L, Falcone JF, Stengel PW, Cohen ML, et al. Investigations into the physiological role of muscarinic M2 and M4 muscarinic and M4 receptor subtypes using receptor knockout mice. Life Sci. 2001;68:2473–2479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

