Repression of smoothened by patched-dependent (pro-)vitamin D3 secretion
- PMID: 16895439
- PMCID: PMC1502141
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040232
Repression of smoothened by patched-dependent (pro-)vitamin D3 secretion
Abstract
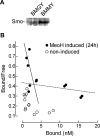
The developmentally important hedgehog (Hh) pathway is activated by binding of Hh to patched (Ptch1), releasing smoothened (Smo) and the downstream transcription factor glioma associated (Gli) from inhibition. The mechanism behind Ptch1-dependent Smo inhibition remains unresolved. We now show that by mixing Ptch1-transfected and Ptch1 small interfering RNA-transfected cells with Gli reporter cells, Ptch1 is capable of non-cell autonomous repression of Smo. The magnitude of this non-cell autonomous repression of Smo activity was comparable to the fusion of Ptch1-transfected cell lines and Gli reporter cell lines, suggesting that it is the predominant mode of action. CHOD-PAP analysis of medium conditioned by Ptch1-transfected cells showed an elevated 3beta-hydroxysteroid content, which we hypothesized to mediate the Smo inhibition. Indeed, the inhibition of 3beta-hydroxysteroid synthesis impaired Ptch1 action on Smo, whereas adding the 3beta-hydroxysteroid (pro-)vitamin D3 to the medium effectively inhibited Gli activity. Vitamin D3 bound to Smo with high affinity in a cyclopamine-sensitive manner. Treating zebrafish embryos with vitamin D3 mimicked the smo(-/-) phenotype, confirming the inhibitory action in vivo. Hh activates its signalling cascade by inhibiting Ptch1-dependent secretion of the 3beta-hydroxysteroid (pro-)vitamin D3. This action not only explains the seemingly contradictory cause of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (SLOS), but also establishes Hh as a unique morphogen, because binding of Hh on one cell is capable of activating Hh-dependent signalling cascades on other cells.
Figures






Comment in
-
Inhibiting hedgehog: new insights into a developmentally important signaling pathway.PLoS Biol. 2006 Aug;4(8):e258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040258. Epub 2006 Jul 18. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 20076617 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bijlsma MF, Spek CA, Peppelenbosch MP. Hedgehog: An unusual signal transducer. Bioessays. 2004;26:387–394. - PubMed
-
- Ingham PW, Taylor AM, Nakano Y. Role of the Drosophila patched gene in positional signalling. Nature. 1991;353:184–187. - PubMed
-
- Marigo V, Davey RA, Zuo Y, Cunningham JM, Tabin CJ. Biochemical evidence that patched is the Hedgehog receptor. Nature. 1996;384:176–179. - PubMed
-
- van den Heuvel M, Ingham PW. smoothened encodes a receptor-like serpentine protein required for hedgehog signalling. Nature. 1996;382:547–551. - PubMed
-
- Denef N, Neubuser D, Perez L, Cohen SM. Hedgehog induces opposite changes in turnover and subcellular localization of patched and smoothened. Cell. 2000;102:521–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

