An early role for WNT signaling in specifying neural patterns of Cdx and Hox gene expression and motor neuron subtype identity
- PMID: 16895440
- PMCID: PMC1502144
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040252
An early role for WNT signaling in specifying neural patterns of Cdx and Hox gene expression and motor neuron subtype identity
Abstract
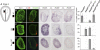
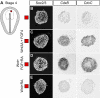
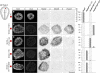
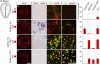
The link between extrinsic signaling, progenitor cell specification and neuronal subtype identity is central to the developmental organization of the vertebrate central nervous system. In the hindbrain and spinal cord, distinctions in the rostrocaudal identity of progenitor cells are associated with the generation of different motor neuron subtypes. Two fundamental classes of motor neurons, those with dorsal (dMN) and ventral (vMN) exit points, are generated over largely non-overlapping rostrocaudal domains of the caudal neural tube. Cdx and Hox genes are important determinants of the rostrocaudal identity of neural progenitor cells, but the link between early patterning signals, neural Cdx and Hox gene expression, and the generation of dMN and vMN subtypes, is unclear. Using an in vitro assay of neural differentiation, we provide evidence that an early Wnt-based program is required to interact with a later retinoic acid- and fibroblast growth factor-mediated mechanism to generate a pattern of Cdx and Hox profiles characteristic of hindbrain and spinal cord progenitor cells that prefigure the generation of vMNs and dMNs.
Figures

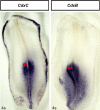
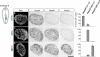
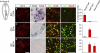
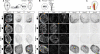

Comment in
-
Wnt sets the stage for spinal cord patterning in the chick.PLoS Biol. 2006 Aug;4(8):e280. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040280. Epub 2006 Jul 18. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 20076624 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Initiating Hox gene expression: in the early chick neural tube differential sensitivity to FGF and RA signaling subdivides the HoxB genes in two distinct groups.Development. 2002 Nov;129(22):5103-15. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.22.5103. Development. 2002. PMID: 12399303
-
Motor neuron columnar fate imposed by sequential phases of Hox-c activity.Nature. 2003 Oct 30;425(6961):926-33. doi: 10.1038/nature02051. Nature. 2003. PMID: 14586461
-
Cdx-Hox code controls competence for responding to Fgfs and retinoic acid in zebrafish neural tissue.Development. 2006 Dec;133(23):4709-19. doi: 10.1242/dev.02660. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Development. 2006. PMID: 17079270
-
Gene expression and regulation of hindbrain and spinal cord development.Front Biosci. 2004 Jan 1;9:117-38. doi: 10.2741/1202. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14766352 Review.
-
Transcriptional codes and the control of neuronal identity.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2002;25:251-81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.25.112701.142916. Epub 2002 Mar 27. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12052910 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the Proteome Dynamics during Development of Neurons Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.J Proteome Res. 2020 Jun 5;19(6):2391-2403. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00070. Epub 2020 May 15. J Proteome Res. 2020. PMID: 32357013 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic extrinsic pacing of the HOX clock in human axial progenitors controls motor neuron subtype specification.Development. 2021 Mar 29;148(6):dev194514. doi: 10.1242/dev.194514. Development. 2021. PMID: 33782043 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-catenin and FGF signalling direct the specification and maintenance of a neuromesodermal axial progenitor in ensembles of mouse embryonic stem cells.Development. 2014 Nov;141(22):4243-53. doi: 10.1242/dev.112979. Development. 2014. PMID: 25371361 Free PMC article.
-
Differential deployment of paralogous Wnt genes in the mouse and chick embryo during development.Evol Dev. 2012 Mar-Apr;14(2):178-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2012.00534.x. Evol Dev. 2012. PMID: 23017026 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of homotypic neural ribbons as a multiplex platform optimized for spinal cord delivery.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 31;10(1):12939. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69274-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32737387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guthrie S. Neuronal development: Putting motor neurons in their place. Curr Biol. 2004;14:R166–168. - PubMed
-
- Jessell TM. Neuronal specification in the spinal cord: Inductive signals and transcriptional codes. Nat Rev Genet. 2000;1:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Lumsden A, Krumlauf R. Patterning the vertebrate neuraxis. Science. 1996;274:1109–1115. - PubMed
-
- Briscoe J, Ericson J. The specification of neuronal identity by graded Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1999;10:353–362. - PubMed
-
- Helms AW, Johnson JE. Specification of dorsal spinal cord interneurons. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:42–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

