Tomosyn inhibits synaptic vesicle priming in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 16895441
- PMCID: PMC1514790
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040261
Tomosyn inhibits synaptic vesicle priming in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
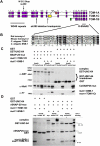
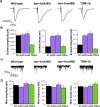
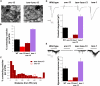
Caenorhabditis elegans TOM-1 is orthologous to vertebrate tomosyn, a cytosolic syntaxin-binding protein implicated in the modulation of both constitutive and regulated exocytosis. To investigate how TOM-1 regulates exocytosis of synaptic vesicles in vivo, we analyzed C. elegans tom-1 mutants. Our electrophysiological analysis indicates that evoked postsynaptic responses at tom-1 mutant synapses are prolonged leading to a two-fold increase in total charge transfer. The enhanced response in tom-1 mutants is not associated with any detectable changes in postsynaptic response kinetics, neuronal outgrowth, or synaptogenesis. However, at the ultrastructural level, we observe a concomitant increase in the number of plasma membrane-contacting vesicles in tom-1 mutant synapses, a phenotype reversed by neuronal expression of TOM-1. Priming defective unc-13 mutants show a dramatic reduction in plasma membrane-contacting vesicles, suggesting these vesicles largely represent the primed vesicle pool at the C. elegans neuromuscular junction. Consistent with this conclusion, hyperosmotic responses in tom-1 mutants are enhanced, indicating the primed vesicle pool is enhanced. Furthermore, the synaptic defects of unc-13 mutants are partially suppressed in tom-1 unc-13 double mutants. These data indicate that in the intact nervous system, TOM-1 negatively regulates synaptic vesicle priming.
Figures



Comment in
-
Keeping things under control at the neuromuscular junction.PLoS Biol. 2006 Aug;4(8):e289. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040289. Epub 2006 Jul 25. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 20076629 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ferro-Novick S, Jahn R. Vesicle fusion from yeast to man. Nature. 1994;370:191–193. - PubMed
-
- Rothman JE. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994;372:55–63. - PubMed
-
- Sutton RB, Fasshauer D, Jahn R, Brunger AT. Crystal structure of a SNARE complex involved in synaptic exocytosis at 2.4 A resolution. Nature. 1998;395:347–353. - PubMed
-
- Hanson PI, Roth R, Morisaki H, Jahn R, Heuser JE. Structure and conformational changes in NSF and its membrane receptor complexes visualized by quick-freeze/deep-etch electron microscopy. Cell. 1997;90:523–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

