Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation, time-of-flight mass spectrometry in genomics research
- PMID: 16895448
- PMCID: PMC1523240
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020100
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation, time-of-flight mass spectrometry in genomics research
Abstract
The beginning of this millennium has seen dramatic advances in genomic research. Milestones such as the complete sequencing of the human genome and of many other species were achieved and complemented by the systematic discovery of variation at the single nucleotide (SNP) and whole segment (copy number polymorphism) level. Currently most genomics research efforts are concentrated on the production of whole genome functional annotations, as well as on mapping the epigenome by identifying the methylation status of CpGs, mainly in CpG islands, in different tissues. These recent advances have a major impact on the way genetic research is conducted and have accelerated the discovery of genetic factors contributing to disease. Technology was the critical driving force behind genomics projects: both the combination of Sanger sequencing with high-throughput capillary electrophoresis and the rapid advances in microarray technologies were keys to success. MALDI-TOF MS-based genome analysis represents a relative newcomer in this field. Can it establish itself as a long-term contributor to genetics research, or is it only suitable for niche areas and for laboratories with a passion for mass spectrometry? In this review, we will highlight the potential of MALDI-TOF MS-based tools for resequencing and for epigenetics research applications, as well as for classical complex genetic studies, allele quantification, and quantitative gene expression analysis. We will also identify the current limitations of this approach and attempt to place it in the context of other genome analysis technologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

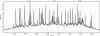


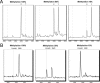
Similar articles
-
Genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms by MALDI mass spectrometry in clinical applications.Clin Biochem. 2005 Apr;38(4):335-50. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2004.12.005. Clin Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15766735 Review.
-
Genomic profiling of CpG methylation and allelic specificity using quantitative high-throughput mass spectrometry: critical evaluation and improvements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(18):e119. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm662. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17855397 Free PMC article.
-
Use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for multiplex genotyping.Adv Clin Chem. 2011;53:1-29. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-385855-9.00001-1. Adv Clin Chem. 2011. PMID: 21404912 Review.
-
Genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms by mass spectrometry.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2002 Nov-Dec;21(6):388-418. doi: 10.1002/mas.1009. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2002. PMID: 12666148 Review.
-
[Analysis of polymorphic markers by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry].Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2005 Apr;22(2):185-8. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 15793781 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
MEK inhibition affects STAT3 signaling and invasion in human melanoma cell lines.Oncogene. 2014 Apr 3;33(14):1850-61. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.131. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23624919 Free PMC article.
-
Increased sensitivity of malaria parasites to common antimalaria drugs after the introduction of artemether-lumefantrine: Implication of policy change and implementation of more effective drugs in fight against malaria.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 20;19(6):e0298585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298585. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38900782 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic identification of placental epigenetic signatures for the noninvasive prenatal detection of Edwards syndrome.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 30;5(11):e15069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015069. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21152411 Free PMC article.
-
A candidate gene study for the association of host single nucleotide polymorphisms with liver cirrhosis risk in chinese hepatitis B patients.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2013 Sep;17(9):681-6. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2013.0058. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2013. PMID: 23844940 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Current and Emerging Technologies for the Analysis of the Genome-Wide and Locus-Specific DNA Methylation Patterns.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1389:395-469. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-11454-0_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36350519
References
-
- Deloukas P, Schuler GD, Gyapay G, Beasley EM, Soderlund C, et al. A physical map of 30,000 human genes. Science. 1998;282:744–746. - PubMed
-
- McPherson JD, Marra M, Hillier L, Waterston RH, Chinwalla A, et al. A physical map of the human genome. The International Human Genome Mapping Consortium. Nature. 2001;409:934–941. - PubMed
-
- Bentley DR, Deloukas P, Dunham A, French L, Gregory SG, et al. The physical maps for sequencing human chromosomes 1, 6, 9, 10, 13, 20, and X. Nature. 2001;409:942–943. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Shoemaker DD, Schadt EE, Armour CD, He YD, Garrett-Engele P, et al. Experimental annotation of the human genome using microarray technology. Nature. 2001;409:922–927. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

