Effectiveness of Haemophilus influenzae type b Conjugate vaccine introduction into routine childhood immunization in Kenya
- PMID: 16896110
- PMCID: PMC1592684
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.296.6.671
Effectiveness of Haemophilus influenzae type b Conjugate vaccine introduction into routine childhood immunization in Kenya
Abstract
Context: Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate vaccine is not perceived as a public health priority in Africa because data on Hib disease burden and vaccine effectiveness are scarce. Hib immunization was introduced in Kenyan infants in 2001.
Objective: To define invasive Hib disease incidence and Hib vaccine program effectiveness in Kenya.
Design, setting, and patients: Culture-based surveillance for invasive Hib disease at Kilifi District Hospital from 2000 through 2005 was linked to demographic surveillance of 38,000 children younger than 5 years in Kilifi District, Kenya. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and Hib vaccination status were determined for children with Hib disease admitted 2002-2005.
Interventions: Introduction of conjugate Hib vaccine within the routine childhood immunization program at ages 6, 10, and 14 weeks beginning November 2001.
Main outcome measures: Incidence of culture-proven Hib invasive disease before and after vaccine introduction and vaccine program effectiveness.
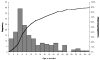
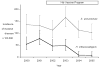
Results: Prior to vaccine introduction, the median age of children with Hib was 8 months; case fatality was 23%. Among children younger than 5 years, the annual incidence of invasive Hib disease 1 year before and 1 and 3 years after vaccine introduction was 66, 47, and 7.6 per 100,000, respectively. For children younger than 2 years, incidence was 119, 82, and 16 per 100,000, respectively. In 2004-2005, vaccine effectiveness was 88% (95% confidence interval, 73%-96%) among children younger than 5 years and 87% (95% confidence interval, 66%-96%) among children younger than 2 years. Of 53 children with Hib admitted during 2002-2005, 29 (55%) were age-ineligible to have received vaccine, 12 (23%) had not been vaccinated despite being eligible, and 12 (23%) had received 2 or more doses of vaccine (2 were HIV positive).
Conclusions: In Kenya, introduction of Hib vaccine into the routine childhood immunization program reduced Hib disease incidence among children younger than 5 years to 12% of its baseline level. This impact was not observed until the third year after vaccine introduction.
Figures
References
-
- Berkley JA, Lowe BS, Mwangi I, et al. Bacteremia among children admitted to a rural hospital in Kenya. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:39–47. - PubMed
-
- Eskola J, Peltola H, Takala AK, et al. Efficacy of Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-diphtheria toxoid conjugate vaccine in infancy. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:717–722. - PubMed
-
- Black SB, Shinefield HR, Fireman B, Hiatt R, Polen M, Vittinghoff E. Efficacy in infancy of oligosaccharide conjugate Haemophilus influenzae type b (HbOC) vaccine in a United States population of 61,080 children. The Northern California Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Center Pediatrics Group. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991;10:97–104. - PubMed
-
- Peltola H, Kilpi T, Anttila M. Rapid disappearance of Haemophilus influenzae type b meningitis after routine childhood immunisation with conjugate vaccines. Lancet. 1992;340:592–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

