CTLA-4 blockade decreases TGF-beta, IDO, and viral RNA expression in tissues of SIVmac251-infected macaques
- PMID: 16896154
- PMCID: PMC1895471
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-010637
CTLA-4 blockade decreases TGF-beta, IDO, and viral RNA expression in tissues of SIVmac251-infected macaques
Erratum in
- Blood. 2009 Oct 1;114(14):3132
Abstract
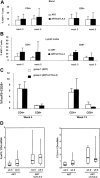
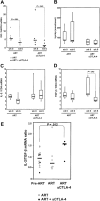
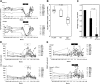
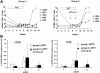
Regulatory T (T(reg)) cells are a subset of CD25(+)CD4(+) T cells that constitutively express high levels of cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) and suppress T-cell activation and effector functions. T(reg) cells are increased in tissues of individuals infected with HIV-1 and macaques infected with simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV(mac251)). In HIV-1 infection, T(reg) cells could exert contrasting effects: they may limit viral replication by decreasing immune activation, or they may increase viral replication by suppressing virusspecific immune response. Thus, the outcome of blocking T(reg) function in HIV/SIV should be empirically tested. Here, we demonstrate that CD25(+) T cells inhibit virus-specific T-cell responses in cultured T cells from blood and lymph nodes of SIV-infected macaques. We investigated the impact of CTLA-4 blockade using the anti-CTLA-4 human antibody MDX-010 in SIV-infected macaques treated with antiretroviral therapy (ART). CTLA-4 blockade decreased expression of the tryptophan-depleting enzyme IDO and the level of the suppressive cytokine transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) in tissues. CTLA-4 blockade was associated with decreased viral RNA levels in lymph nodes and an increase in the effector function of both SIV-specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells. Therefore, blunting T(reg) function in macaques infected with SIV did not have detrimental virologic effects and may provide a valuable approach to complement ART and therapeutic vaccination in the treatment of HIV-1 infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fatal pancreatitis in simian immunodeficiency virus SIV(mac251)-infected macaques treated with 2',3'-dideoxyinosine and stavudine following cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase blockade.J Virol. 2012 Jan;86(1):108-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05609-11. Epub 2011 Oct 19. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22013040 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T-cell markers, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, and virus levels in spleen and gut during progressive simian immunodeficiency virus infection.J Virol. 2007 Nov;81(21):11593-603. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00760-07. Epub 2007 Aug 22. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17715231 Free PMC article.
-
Immune activation driven by CTLA-4 blockade augments viral replication at mucosal sites in simian immunodeficiency virus infection.J Immunol. 2008 Apr 15;180(8):5439-47. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.8.5439. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18390726 Free PMC article.
-
Brain macrophages harbor latent, infectious simian immunodeficiency virus.AIDS. 2019 Dec 1;33 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S181-S188. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002269. AIDS. 2019. PMID: 31789817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hope for an HIV vaccine based on induction of CD8+ T lymphocytes--a review.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2008 Mar;103(2):119-29. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762008000200001. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2008. PMID: 18425263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Complex Dysregulations of CD4 T Cell Subtypes in HIV Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 9;25(14):7512. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147512. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonhuman Primate Testing of the Impact of Different Regulatory T Cell Depletion Strategies on Reactivation and Clearance of Latent Simian Immunodeficiency Virus.J Virol. 2020 Sep 15;94(19):e00533-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00533-20. Print 2020 Sep 15. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32669326 Free PMC article.
-
Functional proteomic analysis for regulatory T cell surveillance of the HIV-1-infected macrophage.J Proteome Res. 2010 Dec 3;9(12):6759-73. doi: 10.1021/pr1009178. Epub 2010 Nov 4. J Proteome Res. 2010. PMID: 20954747 Free PMC article.
-
Exacerbated AIDS Progression by PD-1 Blockade during Therapeutic Vaccination in Chronically Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques after Interruption of Antiretroviral Therapy.J Virol. 2022 Feb 9;96(3):e0178521. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01785-21. Epub 2021 Nov 24. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34818070 Free PMC article.
-
Fatal pancreatitis in simian immunodeficiency virus SIV(mac251)-infected macaques treated with 2',3'-dideoxyinosine and stavudine following cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase blockade.J Virol. 2012 Jan;86(1):108-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05609-11. Epub 2011 Oct 19. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22013040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salomon B, Bluestone JA. Complexities of CD28/B7: CTLA-4 costimulatory pathways in autoimmunity and transplantation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19: 225-252. - PubMed
-
- Thompson CB, Allison JP. The emerging role of CTLA-4 as an immune attenuator. Immunity. 1997;7: 445-450. - PubMed
-
- Hueber AJ, Matzkies FG, Rahmeh M, et al. CTLA-4 lacking the cytoplasmic domain costimulates IL-2 production in T-cell hybridomas. Immunol Cell Biol. 2006;84: 51-58. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

