Efficacy and safety of coadministered amlodipine and atorvastatin in patients with hypertension and dyslipidemia: results of the AVALON trial
- PMID: 16896273
- PMCID: PMC8109721
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2006.05636.x
Efficacy and safety of coadministered amlodipine and atorvastatin in patients with hypertension and dyslipidemia: results of the AVALON trial
Abstract
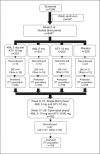
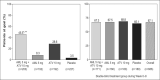
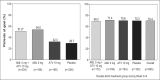
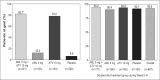
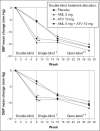
The AVALON study was a randomized, multicenter trial to assess the efficacy and safety of coadministered amlodipine and atorvastatin in patients with hypertension and dyslipidemia. Phase one was an 8-week, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled period whereby patients received amlodipine 5 mg, atorvastatin 10 mg, amlodipine 5 mg and atorvastatin 10 mg, or placebo. Thereafter, all patients received single-blind amlodipine 5 mg and atorvastatin 10 mg for 8-weeks, followed by 12 weeks of open-label treatment where doses could be titrated to improve low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and blood pressure control. A total of 847 patients entered the double-blind phase. At Week 8, 45% of the patients receiving amlodipine 5 mg and atorvastatin 10 mg reached both their blood pressure and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goals, compared with 8.3% with amlodipine (p < 0.001), 28.6% with atorvastatin (p < 0.001), and 3.5% with placebo. At 28 weeks, 67.1% of patients coadministered amlodipine and atorvastatin (mean doses, 7.6 mg and 28.4 mg, respectively) achieved both targets. Framingham estimated 10-year risk of coronary heart disease declined from baseline levels of 15.1% to 6.9% at Week 28. Following coadministered treatment, the adverse events reported were similar to either agent alone. Concomitant administration of amlodipine and atorvastatin is an effective and well tolerated treatment for coexisting hypertension and dyslipidemia.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . The World Health Report 2003: Shaping the Future. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2003.
-
- Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics‐2006 update. A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2006;113:e85–el51. - PubMed
-
- Flack JM, Neaton J, Grimm R Jr, et al. Blood pressure and mortality among men with prior myocardial infarction. Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial Research Group. Circulation. 1995;92:2437–2445. - PubMed
-
- Greenlund KJ, Zheng ZJ, Keenan NL, et al. Trends in selfreported multiple cardiovascular disease risk factors among adults in the United States, 1991–1999. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:181–188. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB. Fifty years of Framingham Study contributions to understanding hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2000;14:83–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

