ERP evidence of atypical face processing in young children with autism
- PMID: 16897400
- PMCID: PMC2989721
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-006-0126-x
ERP evidence of atypical face processing in young children with autism
Abstract
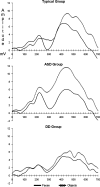
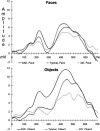
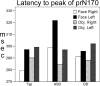
Autism involves a basic impairment in social cognition. This study investigated early stage face processing in young children with autism by examining the face-sensitive early negative event-related brain potential component in 3-4 year old children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), typical development, and developmental delay. Results indicated that children with ASD showed a slower electrical brain response to faces and a larger amplitude response to objects compared to children with typical development and developmental delay. These findings indicate that children with ASD have a disordered pattern of brain responses to faces and objects at an early age.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The development of face processing in autism.J Autism Dev Disord. 2006 Apr;36(3):381-94. doi: 10.1007/s10803-006-0076-3. J Autism Dev Disord. 2006. PMID: 16572261 Review.
-
Neurocognitive and electrophysiological evidence of altered face processing in parents of children with autism: implications for a model of abnormal development of social brain circuitry in autism.Dev Psychopathol. 2005 Summer;17(3):679-97. doi: 10.1017/S0954579405050327. Dev Psychopathol. 2005. PMID: 16262987
-
Young children with autism show atypical brain responses to fearful versus neutral facial expressions of emotion.Dev Sci. 2004 Jun;7(3):340-59. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-7687.2004.00352.x. Dev Sci. 2004. PMID: 15595374
-
Atypical face versus object processing and hemispheric asymmetries in 10-month-old infants at risk for autism.Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Nov 15;66(10):950-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.07.031. Epub 2009 Sep 18. Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19765688 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired face processing in autism: fact or artifact?J Autism Dev Disord. 2006 Jan;36(1):91-106. doi: 10.1007/s10803-005-0050-5. J Autism Dev Disord. 2006. PMID: 16477517 Review.
Cited by
-
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Fragile X Syndrome (FXS): Two Overlapping Disorders Reviewed through Electroencephalography-What Can be Interpreted from the Available Information?Brain Sci. 2015 Mar 27;5(2):92-117. doi: 10.3390/brainsci5020092. Brain Sci. 2015. PMID: 25826237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visual event-related potentials to biological motion stimuli in autism spectrum disorders.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2014 Aug;9(8):1214-22. doi: 10.1093/scan/nst103. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 23887808 Free PMC article.
-
A single-session behavioral protocol for successful event-related potential recording in children with neurodevelopmental disorders.Dev Psychobiol. 2021 Nov;63(7):e22194. doi: 10.1002/dev.22194. Dev Psychobiol. 2021. PMID: 34674246 Free PMC article.
-
The implications of social neuroscience for social disability.J Autism Dev Disord. 2012 Jun;42(6):1256-62. doi: 10.1007/s10803-012-1514-z. J Autism Dev Disord. 2012. PMID: 22456816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Face perception and learning in autism spectrum disorders.Q J Exp Psychol (Hove). 2017 May;70(5):970-986. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2016.1151059. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Q J Exp Psychol (Hove). 2017. PMID: 26886246 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adrien J, Faure M, Perrot A, Hameury L, Garreau B, Barthelemy C, Sauvage D. Autism and family home movies: preliminary findings. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 1991;21(1):43–49. - PubMed
-
- Baron-Cohen S. Mindblindness, An essay on autism and theory of mind. Bradford/MIT Press; Cambridge, MA: 1995.
-
- Begleiter H, Porjesz B, Wang W. Event-related brain potentials differentiate priming and recognition to familiar and unfamiliar faces. Electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology. 1995;94(1):41–49. - PubMed
-
- Bentin S, Deouell LY. Structural encoding and identification in face processing, ERP evidence for separate mechanisms. Cognitive Neuropsychology. 2000;17:35–54. - PubMed
-
- Bentin S, Deouell LY, Soroker N. Selective visual streaming in face recognition: evidence from developmental prosopagnosia. Neuroreport. 1999;10(4):823–827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

