Role of chromosome stability and telomere length in the production of viable cell lines for somatic cell nuclear transfer
- PMID: 16899119
- PMCID: PMC1590017
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-6-41
Role of chromosome stability and telomere length in the production of viable cell lines for somatic cell nuclear transfer
Abstract
Background: Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) provides an appealing alternative for the preservation of genetic material in non-domestic and endangered species. An important prerequisite for successful SCNT is the availability of good quality donor cells, as normal embryo development is dependent upon proper reprogramming of the donor genome so that embryonic genes can be appropriately expressed. The characteristics of donor cell lines and their ability to produce embryos by SCNT were evaluated by testing the effects of tissue sample collection (DART biopsy, PUNCH biopsy, post-mortem EAR sample) and culture initiation (explant, collagenase digestion) techniques.
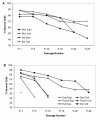
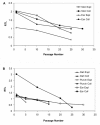
Results: Differences in initial sample size based on sample collection technique had an effect on the amount of time necessary for achieving primary confluence and the number of population doublings (PDL) produced. Thus, DART and PUNCH biopsies resulted in cultures with decreased lifespans (<30 PDL) accompanied by senescence-like morphology and decreased normal chromosome content (<40% normal cells at 20 PDL) compared to the long-lived (>50 PDL) and chromosomally stable (>70% normal cells at 20 PDL) cultures produced by post-mortem EAR samples. Chromosome stability was influenced by sample collection technique and was dependent upon the culture's initial telomere length and its rate of shortening over cell passages. Following SCNT, short-lived cultures resulted in significantly lower blastocyst development (< or = 0.9%) compared to highly proliferative cultures (11.8%). Chromosome stability and sample collection technique were significant factors in determining blastocyst development outcome.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate the influence of culture establishment techniques on cell culture characteristics, including the viability, longevity and normality of cells. The identification of a quantifiable marker associated with SCNT embryo developmental potential, chromosome stability, provides a means by which cell culture conditions can be monitored and improved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A comparative approach to somatic cell nuclear transfer in the rhesus monkey.Hum Reprod. 2006 Oct;21(10):2564-71. doi: 10.1093/humrep/del216. Epub 2006 Jun 22. Hum Reprod. 2006. PMID: 16793991
-
The impact of chromosomal alteration on embryo development.Theriogenology. 2006 Jan 7;65(1):166-77. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2005.09.031. Epub 2005 Nov 8. Theriogenology. 2006. PMID: 16280155 Review.
-
Preimplantational embryo development and incidence of blastomere apoptosis in bovine somatic cell nuclear transfer embryos reconstructed with long-term cultured donor cells.Theriogenology. 2004 Aug;62(3-4):512-21. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2003.11.022. Theriogenology. 2004. PMID: 15226007
-
Blastocysts derived from adult fibroblasts of a rhesus monkey ( Macaca mulatta) using interspecies somatic cell nuclear transfer.Zygote. 2011 Aug;19(3):199-204. doi: 10.1017/S0967199411000232. Epub 2011 May 4. Zygote. 2011. PMID: 21554770
-
Epigenetic reprogramming in embryonic and foetal development upon somatic cell nuclear transfer cloning.Reproduction. 2008 Feb;135(2):151-63. doi: 10.1530/REP-07-0397. Reproduction. 2008. PMID: 18239046 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue sampling methods and standards for vertebrate genomics.Gigascience. 2012 Jul 12;1(1):8. doi: 10.1186/2047-217X-1-8. Gigascience. 2012. PMID: 23587255 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Evaluation of Achillea Millefolium on the Production and Stimulation of Human Skin Fibroblast Cells (HFS-PI-16).Med Arch. 2015 Aug;69(4):212-7. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2015.69.212-217. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Med Arch. 2015. PMID: 26543303 Free PMC article.
-
Cytogentic analysis of human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) in early and late passages using both karyotyping and comet assay techniques.Cytotechnology. 2014 Oct;66(5):815-22. doi: 10.1007/s10616-013-9630-y. Epub 2013 Aug 31. Cytotechnology. 2014. PMID: 23996453 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery of fibroblast-like cells from refrigerated goat skin up to 41 d of animal death.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015 May;51(5):463-9. doi: 10.1007/s11626-014-9856-9. Epub 2014 Dec 25. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015. PMID: 25539865
-
Effect of postmortem time interval on in vitro culture potential of goat skin tissues stored at room temperature.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2012 Sep;48(8):478-82. doi: 10.1007/s11626-012-9539-3. Epub 2012 Aug 8. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2012. PMID: 22872525
References
-
- Wildt DE. Genetic resource banks for conserving wildlife species: justification, examples and becoming organized on a global basis. Anim Reprod Sci. 1992;28:247–257. doi: 10.1016/0378-4320(92)90111-P. - DOI
-
- Pignolo RJ, Cristofalo VJ, Rotenberg MO. Senescent WI-38 cells fail to express EPC-1, a gene induced in young cells upon entry into the G0 state. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:8949–8957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

