HLA-DR expression on monocytes and systemic inflammation in patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms
- PMID: 16899122
- PMCID: PMC1751002
- DOI: 10.1186/cc5017
HLA-DR expression on monocytes and systemic inflammation in patients with ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms
Abstract
Introduction: Mortality from ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (RAAA) remains high. Severe systemic inflammation, leading to multi-organ failure, often occurs in these patients. In this study we describe the level of HLA-DR expression in a consecutive group of patients following surgery for RAAA and compare results between survivors and non-survivors. A similar comparison is made for IL-6, IL-10 levels and SOFA-scores.
Methods: This is a prospective observational study. Patients with RAAA were prospectively analyzed. Blood samples were collected on day 1, 3, 5, 7, 10 and 14. The fraction of CD-14 positive monocytes expressing HLA-DR was measured by flow-cytometry. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels were measured by ELISA.
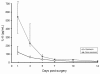
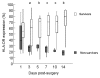
Results: Thirty patients with a median age of 70 years were included. There were 27 (90%) men. Six patients died from multiple organ failure, all other patients survived. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) scores were significantly higher in non-survivors on day 1 through 14. HLA-DR expression on monocytes was significantly lower on day 3, 5, 7, 10 and 14 in non-survivors. Interleukin-6 and IL-10 levels were significantly higher in non-survivors on day 1 and day 1 and 3 respectively.
Conclusions: HLA-DR expression on monocytes was decreased, especially in non-survivors. All patients with RAAA displayed a severe inflammatory and anti-inflammatory response with an increased production of IL-6 and IL-10. Poor outcome is associated with high levels of IL-6 and IL-10 and a high SOFA score in the first three days after surgery, while low levels of HLA-DR expression are observed from day three after RAAA repair.
Figures
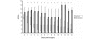

Similar articles
-
Longitudinal monocyte human leukocyte antigen-DR expression is a prognostic marker in critically ill patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis.Liver Int. 2009 Apr;29(4):536-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01870.x. Epub 2008 Sep 15. Liver Int. 2009. PMID: 18795898
-
Up-regulation of interleukin-10 mRNA expression in peripheral leukocytes predicts poor outcome and diminished human leukocyte antigen-DR expression on monocytes in septic patients.J Surg Res. 2008 Jun 1;147(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2007.07.009. Epub 2007 Aug 20. J Surg Res. 2008. PMID: 17720196
-
The anti-inflammatory response dominates after septic shock: association of low monocyte HLA-DR expression and high interleukin-10 concentration.Immunol Lett. 2004 Sep;95(2):193-8. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2004.07.009. Immunol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15388260
-
[Monocyte HLA-DR expression as predictors of clinical outcome for patients with sepsis].Nihon Rinsho. 2004 Dec;62(12):2281-4. Nihon Rinsho. 2004. PMID: 15597796 Review. Japanese.
-
Assessment of immunological status in the critically ill.Minerva Anestesiol. 2000 May;66(5):351-7. Minerva Anestesiol. 2000. PMID: 10965715 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a Modular Assay for Detailed Immunophenotyping of Peripheral Human Whole Blood Samples by Multicolor Flow Cytometry.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 11;17(8):1316. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081316. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27529227 Free PMC article.
-
Score performance of SAPS 2 and SAPS 3 in combination with biomarkers IL-6, PCT or CRP.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 3;15(9):e0238587. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238587. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32881963 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine 5'-Monophosphate-to-Threonine Ratio Promotes Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms via Up-Regulation of HLA-DR on Natural Killer Cells: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomized Analysis.Biomedicines. 2024 May 25;12(6):1179. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061179. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927386 Free PMC article.
-
Translocation of bacterial NOD2 agonist and its link with inflammation.Crit Care. 2009;13(4):R124. doi: 10.1186/cc7980. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Crit Care. 2009. PMID: 19638210 Free PMC article.
-
Dampened Inflammatory Signalling and Myeloid-Derived Suppressor-Like Cell Accumulation Reduces Circulating Monocytic HLA-DR Density and May Associate With Malignancy Risk in Long-Term Renal Transplant Recipients.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 1;13:901273. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.901273. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844527 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

