Two uniquely arranged thyroid hormone response elements in the far upstream 5' flanking region confer direct thyroid hormone regulation to the murine cholesterol 7alpha hydroxylase gene
- PMID: 16899449
- PMCID: PMC1557806
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl506
Two uniquely arranged thyroid hormone response elements in the far upstream 5' flanking region confer direct thyroid hormone regulation to the murine cholesterol 7alpha hydroxylase gene
Abstract
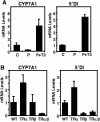
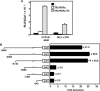
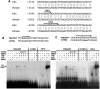
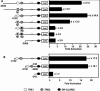
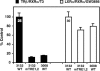
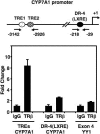
Cholesterol 7alpha hydroxlyase (CYP7A1) is a key enzyme in cholesterol catabolism to bile acids and its activity is important for maintaining appropriate cholesterol levels. The murine CYP7A1 gene is highly inducible by thyroid hormone in vivo and there is an inverse relationship between thyroid hormone and serum cholesterol. Eventhough gene expression has been shown to be upregulated, whether the induction was mediated through a direct effect of thyroid hormone on the CYP7A1 promoter has never been established. Using gene targeted mice, we show that either of the two TR isoforms are sufficient to maintain normal hepatic CYP7A1 expression but a loss of both results in a significant decrease in expression. We also identified two new functional thyroid hormone receptor-binding sites in the CYP7A1 5' flanking sequence located 3 kb upstream from the transcription start site. One site is a DR-0, which is an unusual type of TR response element, and the other consists of only a single recognizable half site that is required for TR/retinoid X receptor (RXR) binding. These two independent TR-binding sites are closely spaced and both are required for full induction of the CYP7A1 promoter by thyroid hormone, although the DR-0 site was more crucial.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cross-talk between thyroid hormone receptor and liver X receptor regulatory pathways is revealed in a thyroid hormone resistance mouse model.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jan 6;281(1):295-302. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507877200. Epub 2005 Oct 31. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16260782
-
The atypical interaction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha with liver X receptor alpha antagonizes the stimulatory effect of their respective ligands on the murine cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene promoter.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jul 11;1583(2):229-36. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(02)00217-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12117567
-
A distinct thyroid hormone response element mediates repression of the human cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) gene promoter.Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Jan;16(1):14-23. doi: 10.1210/mend.16.1.0751. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 11773435
-
Regulation of cholesterol-7alpha-hydroxylase: BAREly missing a SHP.J Lipid Res. 2002 Apr;43(4):533-43. J Lipid Res. 2002. PMID: 11907135 Review.
-
Multiple mechanisms for regulation of the transcriptional activity of thyroid hormone receptors.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2000 Jan;1(1-2):9-18. doi: 10.1023/a:1010052101214. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2000. PMID: 11704997 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Novel transcriptome assembly and comparative toxicity pathway analysis in mahi-mahi (Coryphaena hippurus) embryos and larvae exposed to Deepwater Horizon oil.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 15;7:44546. doi: 10.1038/srep44546. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28295044 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of thyroid hormone receptor binding sites in developing mouse cerebellum.BMC Genomics. 2013 May 23;14:341. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-341. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23701648 Free PMC article.
-
The thyroid hormone mimetic compound KB2115 lowers plasma LDL cholesterol and stimulates bile acid synthesis without cardiac effects in humans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Jan 15;105(2):663-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705286104. Epub 2007 Dec 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18160532 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
3,5-Diiodo-L-thyronine (3,5-t2) exerts thyromimetic effects on hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis, body composition, and energy metabolism in male diet-induced obese mice.Endocrinology. 2015 Jan;156(1):389-99. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1604. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25322465 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid hormone-regulated gene expression in juvenile mouse liver: identification of thyroid response elements using microarray profiling and in silico analyses.BMC Genomics. 2011 Dec 29;12:634. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-634. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22206413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiang J.Y. Bile acid regulation of gene expression: roles of nuclear hormone receptors. Endocr. Rev. 2002;23:443–463. - PubMed
-
- Peet D.J., Turley S.D., Ma W., Janowski B.A., Lobaccaro J.M., Hammer R.E., Mangelsdorf D.J. Cholesterol and bile acid metabolism are impaired in mice lacking the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXR alpha. Cell. 1998;93:693–704. - PubMed
-
- Lehmann J.M., Kliewer S.A., Moore L.B., Smith-Oliver T.A., Oliver B.B., Su J.L., Sundseth S.S., Winegar D.A., Blanchard D.E., Spencer T.A., et al. Activation of the nuclear receptor LXR by oxysterols defines a new hormone response pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:3137–3140. - PubMed
-
- Janowski B.A., Willy P.J., Devi T.R., Falck J.R., Mangelsdorf D.J. An oxysterol signalling pathway mediated by the nuclear receptor LXR alpha. Nature. 1996;383:728–731. - PubMed
-
- Lu T.T., Makishima M., Repa J.J., Schoonjans K., Kerr T.A., Auwerx J., Mangelsdorf D.J. Molecular basis for feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis by nuclear receptors. Mol. Cell. 2000;6:507–515. - PubMed

