Central and medial amygdaloid brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling plays a critical role in alcohol-drinking and anxiety-like behaviors
- PMID: 16899727
- PMCID: PMC6673799
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4988-05.2006
Central and medial amygdaloid brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling plays a critical role in alcohol-drinking and anxiety-like behaviors
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2010 May 26;30(21):7447-8
Abstract
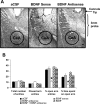
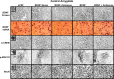
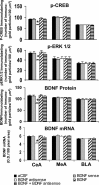
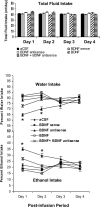
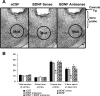
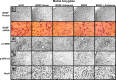
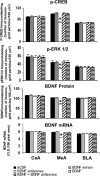
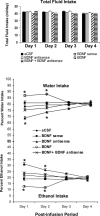
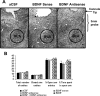
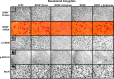
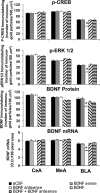
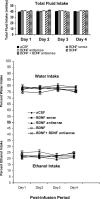
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a member of the nerve growth factor family of neurotrophins and plays a vital role in synaptic plasticity. This study investigated the involvement of the amygdaloid BDNF system in molecular mechanisms underlying anxiety and alcohol-drinking behaviors. Male Sprague Dawley rats were cannulated targeting central amygdala (CeA), medial amygdala (MeA), or basolateral amygdala (BLA), and BDNF expression was manipulated using an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide (ODN) strategy. Anxiety-like and alcohol-drinking behaviors were measured after infusion of BDNF sense and antisense ODNs with or without BDNF coinfusion, using the elevated plus-maze test and two-bottle free-choice paradigm, respectively. Here we report that BDNF antisense ODN infusions into the CeA and MeA, but not BLA, provoked anxiety-like behaviors in rats, which were rescued by BDNF coinfusion. The levels of BDNF, p-ERK1/2 (phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2), and p-CREB (phosphorylated cAMP responsive-element binding protein) were decreased by BDNF antisense, but not by sense, ODN infusions, which were restored to normal after BDNF coinfusions. Furthermore, BDNF antisense ODN infusions into the CeA or MeA, but not into BLA, increased alcohol intake, which was attenuated by BDNF coinfusions. These novel results suggest that decreased BDNF levels in the CeA and MeA, but not in the BLA, are crucial in regulating alcohol-drinking and anxiety-like behaviors in rats.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential role of adolescent alcohol exposure-induced amygdaloid histone modifications in anxiety and alcohol intake during adulthood.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Oct;82:607-619. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.03.019. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25814047 Free PMC article.
-
The role of amygdaloid brain-derived neurotrophic factor, activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein and dendritic spines in anxiety and alcoholism.Addict Biol. 2011 Apr;16(2):238-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2010.00275.x. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Addict Biol. 2011. PMID: 21182574 Free PMC article.
-
Innate differences in the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the regions within the extended amygdala between alcohol preferring and nonpreferring rats.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008 Jun;32(6):909-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00650.x. Epub 2008 Apr 26. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008. PMID: 18445109
-
The anxious amygdala: CREB signaling and predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism.J Clin Invest. 2005 Oct;115(10):2697-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI26436. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16200206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BDNF mechanisms in late LTP formation: A synthesis and breakdown.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:664-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23831365 Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol induced depressive-like behavior is associated with a reduction in hippocampal BDNF.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2011 Dec;100(2):253-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.08.014. Epub 2011 Sep 10. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2011. PMID: 21930150 Free PMC article.
-
Homer2 regulates alcohol and stress cross-sensitization.Addict Biol. 2016 May;21(3):613-33. doi: 10.1111/adb.12252. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Addict Biol. 2016. PMID: 25916683 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Antidepressant Treatment in Normal Mice Induces Anxiety and Impairs Stress-coping Ability.Exp Neurobiol. 2015 Jun;24(2):156-68. doi: 10.5607/en.2015.24.2.156. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Exp Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 26113795 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture Alleviates Anxiety and 22-kHz Ultrasonic Vocalizations in Rats Subjected to Repeated Alcohol Administration by Modulating the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor/Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 14;22(8):4037. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084037. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919862 Free PMC article.
-
Effector immediate-early gene arc in the amygdala plays a critical role in alcoholism.J Neurosci. 2008 Mar 5;28(10):2589-600. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4752-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18322102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agassandian K, Gedney M, Cassell MD (2006). Neurotrophic factors in the central nucleus of amygdala may be organized to provide substrates for associative learning. Brain Res 1076:78–86. - PubMed
-
- Barnea A, Roberts J (2001). Induction of functional and morphological expression of neuropeptide Y (NPY) in cortical cultures by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): evidence for a requirement for extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK)-dependent and ERK-independent mechanisms. Brain Res 919:57–69. - PubMed
-
- Bibel M, Barde YA (2000). Neurotrophins: key regulators of cell fate and cell shape in the vertebrate nervous system. Genes Dev 14:2919–2937. - PubMed
-
- Davis M (1997). Neurobiology of fear responses: the role of the amygdala. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 9:382–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
