Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces interleukin-32 production through a caspase- 1/IL-18/interferon-gamma-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 16903774
- PMCID: PMC1539091
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030277
Mycobacterium tuberculosis induces interleukin-32 production through a caspase- 1/IL-18/interferon-gamma-dependent mechanism
Abstract
Background: Interleukin (IL)-32 is a newly described proinflammatory cytokine that seems likely to play a role in inflammation and host defense. Little is known about the regulation of IL-32 production by primary cells of the immune system.
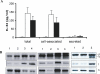
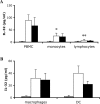
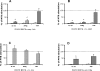
Methods and findings: In the present study, freshly obtained human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stimulated with different Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists, and gene expression and synthesis of IL-32 was determined. We demonstrate that the TLR4 agonist lipopolysaccharide induces moderate (4-fold) production of IL-32, whereas agonists of TLR2, TLR3, TLR5, or TLR9, each of which strongly induced tumor necrosis factor alpha and IL-6, did not stimulate IL-32 production. However, the greatest amount of IL-32 was induced by the mycobacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis and M. bovis BCG (20-fold over unstimulated cells). IL-32-induced synthesis by either lipopolysaccharide or mycobacteria remains entirely cell-associated in monocytes; moreover, steady-state mRNA levels are present in unstimulated monocytes without translation into IL-32 protein, similar to other cytokines lacking a signal peptide. IL-32 production induced by M. tuberculosis is dependent on endogenous interferon-gamma (IFNgamma); endogenous IFNgamma is, in turn, dependent on M. tuberculosis-induced IL-18 via caspase-1.
Conclusions: In conclusion, IL-32 is a cell-associated proinflammatory cytokine, which is specifically stimulated by mycobacteria through a caspase-1- and IL-18-dependent production of IFNgamma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kim SH, Han SY, Azam T, Yoon DY, Dinarello CA. Interleukin-32: A cytokine and inducer of TNF-alpha. Immunity. 2005;22:131–142. - PubMed
-
- Ottenhoff TH, Verreck FAW, Hoeve MA, van de Vosse E. Control of human host immunity to mycobacteria. Tuberculosis. 2005;85:53–64. - PubMed
-
- Murray HW, Scavuzzo D, Jacobs JL, Kaplan MH, Libby DM, et al. In vitro and in vivo activation of human mononuclear phagocytes by interferon-g. J Immunol. 1987;138:2457–2462. - PubMed
-
- Perrusia B, Kobayashi M, Rossi ME, Anegon I, Trinchieri G. Immune interferon enhances functional properties of human granulocytes: Role of Fc receptors and effect of lymphotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1987;138:765–774. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

