The structural basis for promoter -35 element recognition by the group IV sigma factors
- PMID: 16903784
- PMCID: PMC1540707
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040269
The structural basis for promoter -35 element recognition by the group IV sigma factors
Abstract
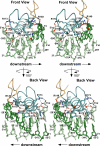
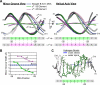
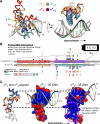
The control of bacterial transcription initiation depends on a primary sigma factor for housekeeping functions, as well as alternative sigma factors that control regulons in response to environmental stresses. The largest and most diverse subgroup of alternative sigma factors, the group IV extracytoplasmic function sigma factors, directs the transcription of genes that regulate a wide variety of responses, including envelope stress and pathogenesis. We determined the 2.3-A resolution crystal structure of the -35 element recognition domain of a group IV sigma factor, Escherichia coli sigma(E)4, bound to its consensus -35 element, GGAACTT. Despite similar function and secondary structure, the primary and group IV sigma factors recognize their -35 elements using distinct mechanisms. Conserved sequence elements of the sigma(E) -35 element induce a DNA geometry characteristic of AA/TT-tract DNA, including a rigid, straight double-helical axis and a narrow minor groove. For this reason, the highly conserved AA in the middle of the GGAACTT motif is essential for -35 element recognition by sigma(E)4, despite the absence of direct protein-DNA interactions with these DNA bases. These principles of sigma(E)4/-35 element recognition can be applied to a wide range of other group IV sigma factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
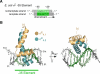


Comment in
-
A bacterial protein puts a new twist on DNA transcription.PLoS Biol. 2006 Sep;4(9):e294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040294. Epub 2006 Aug 15. PLoS Biol. 2006. PMID: 20076632 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Darst SA. Bacterial RNA polymerase. Curr Opinion Struct Biol. 2001;11:155–162. - PubMed
-
- Gross CA, Chan C, Dombroski A, Gruber T, Sharp M, et al. The functional and regulatory roles of sigma factors in transcription. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1998;63:141–155. - PubMed
-
- Murakami K, Darst SA. Bacterial RNA polymerases: The wholo story. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2003;13:31–39. - PubMed
-
- Campbell EA, Muzzin O, Chlenov M, Sun JL, Olson CA, et al. Structure of the bacterial RNA polymerase promoter specificity sigma factor. Mol Cell. 2002;9:527–539. - PubMed
-
- Murakami K, Masuda S, Campbell EA, Muzzin O, Darst SA. Structural basis of transcription initiation: An RNA polymerase holoenzyme/DNA complex. Science. 2002;296:1285–1290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

