Enhanced neutrophil motility by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: the role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PMID: 16903868
- PMCID: PMC1819568
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2006.02448.x
Enhanced neutrophil motility by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: the role of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
Abstract
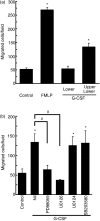
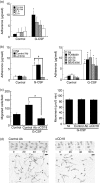
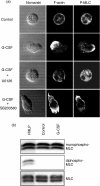
The effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) on human neutrophil motility was studied using videomicroscopy. Stimulation of neutrophils with G-CSF resulted in enhanced motility with morphological change and increased adherence. Enhanced neutrophil motility was detected within 3-5 min after G-CSF stimulation, reached a maximum at 10 min, and was sustained for approximately 35 min. The maximum migration rate was 84.4 +/- 2.9 microm/5 min. A study using the Boyden chamber method revealed that G-CSF-stimulated neutrophils exhibited random migration but not chemotaxis. Enhanced neutrophil motility and morphological change were inhibited by MEK [mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase] inhibitors (PD98059 and U0126), and a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor (wortmannin), but not by a p38 MAPK inhibitor (SB203580). These findings are consistent with the fact that G-CSF selectively activates MEK/ERK and PI3K, but not p38, in neutrophils. MEK/ERK activation was associated with G-CSF-induced redistribution of F-actin and phosphorylated myosin light chain. Enhanced neutrophil motility was observed even in the presence of neutralizing anti-CD18 antibody, which prevented cell adherence. These findings indicate that G-CSF induces human neutrophil migration via activation of MEK/ERK and PI3K.
Figures





References
-
- Yuo A, Kitagawa S, Ohsaka A, et al. Recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor as an activator of human granulocytes: potentiation of responses triggered by receptor-mediated agonists and stimulation of C3bi receptor expression and adherence. Blood. 1989;74:2144–9. - PubMed
-
- Ohsaka A, Kitagawa S, Sakamoto S, Miura Y, Takanashi N, Takaku F, Saito M. In vivo activation of human neutrophil functions by administration of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with malignant lymphoma. Blood. 1989;74:2743–8. - PubMed
-
- Demetri GD, Griffin JD. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and its receptor. Blood. 1991;78:2791–808. - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa T, Suzuki K, Sakamoto C, Ohta K, Nishiki S, Hino M, Tatsumi N, Kitagawa S. Expression of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family members in human neutrophils: up-regulation of cIAP2 by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and overexpression of cIAP2 in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Blood. 2003;101:1164–71. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K, Hino M, Hato F, Tatsumi N, Kitagawa S. Cytokine-specific activation of distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase subtype cascades in human neutrophils stimulated by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and tumor necrosis factor-α. Blood. 1999;93:341–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

