A DNA prime-oral Listeria boost vaccine in rhesus macaques induces a SIV-specific CD8 T cell mucosal response characterized by high levels of alpha4beta7 integrin and an effector memory phenotype
- PMID: 16904153
- PMCID: PMC1635491
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.06.036
A DNA prime-oral Listeria boost vaccine in rhesus macaques induces a SIV-specific CD8 T cell mucosal response characterized by high levels of alpha4beta7 integrin and an effector memory phenotype
Abstract
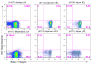
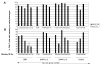
In this study in Rhesus macaques, we tested whether IL-12 or IL-15 in a DNA prime-oral Listeria boost amplifies the SIV-Gag-specific CD8 mucosal response. SIV-specific CD8 T cells were demonstrated in the peripheral blood (PB) in all test vaccine groups, but not the control group. SIV-Gag-specific CD8 T cells in the PB expressed alpha4beta7 integrin, the gut-homing receptor; a minor subset co-express alphaEbeta7 integrin. SIV-Gag-specific CD8 T cells were also detected in the gut tissue, intraepithelial (IEL) and lamina propria lymphocytes (LPL) of the duodenum and ileum. These cells were characterized by high levels of beta7 integrin expression and a predominance of the effector memory phenotype. Neither Il-12 nor IL-15 amplified the frequency of SIV-specific CD8 T cells in the gut. Thus, the DNA prime-oral Listeria boost strategy induced a mucosal SIV-Gag-specific CD8 T cell response characterized by expression of the alpha4beta7 integrin gut-homing receptor.
Figures














Similar articles
-
Mucosal priming of simian immunodeficiency virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses in rhesus macaques by the Salmonella type III secretion antigen delivery system.J Virol. 2003 Feb;77(4):2400-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.4.2400-2409.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12551977 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant rubella vectors elicit SIV Gag-specific T cell responses with cytotoxic potential in rhesus macaques.Vaccine. 2015 Apr 27;33(18):2167-74. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.02.067. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 25802183 Free PMC article.
-
DNA prime Listeria boost induces a cellular immune response to SIV antigens in the rhesus macaque model that is capable of limited suppression of SIV239 viral replication.Virology. 2005 Mar 1;333(1):88-101. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.12.026. Virology. 2005. PMID: 15708595
-
Integrin α4β7 in HIV-1 infection: A critical review.J Leukoc Biol. 2020 Aug;108(2):627-632. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4MR0120-208R. Epub 2020 Apr 9. J Leukoc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32272507 Review.
-
A Yin and Yang in Epithelial Immunology: The Roles of the αE(CD103)β7 Integrin in T Cells.J Invest Dermatol. 2018 Jan;138(1):23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2017.05.026. Epub 2017 Sep 21. J Invest Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 28941625 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct Humoral and Cellular Immunity Induced by Alternating Prime-boost Vaccination Using Plasmid DNA and Live Viral Vector Vaccines Expressing the E Protein of Dengue Virus Type 2.Immune Netw. 2011 Oct;11(5):268-80. doi: 10.4110/in.2011.11.5.268. Epub 2011 Oct 31. Immune Netw. 2011. PMID: 22194710 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal vaccines: novel strategies and applications for the control of pathogens and tumors at mucosal sites.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(8):2175-87. doi: 10.4161/hv.29269. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25424921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An effective vaccination approach augments anti-HIV systemic and vaginal immunity in mice with decreased HIV-1 susceptible α4β7high CD4+ T cells.Curr HIV Res. 2013 Jan;11(1):56-66. Curr HIV Res. 2013. PMID: 23157585 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous vaccination targeting prostatic acid phosphatase (PAP) using DNA and Listeria vaccines elicits superior anti-tumor immunity dependent on CD4+ T cells elicited by DNA priming.Oncoimmunology. 2018 May 7;7(8):e1456603. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1456603. eCollection 2018. Oncoimmunology. 2018. PMID: 30221049 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes delivery of HPV-16 major capsid protein L1 induces systemic and mucosal cell-mediated CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses after oral immunization.Viral Immunol. 2009 Jun;22(3):195-204. doi: 10.1089/vim.2008.0071. Viral Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19435416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen TM, Sidney J, del Guercio MF, Glickman RL, Lensmeyer GL, Wiebe DA, DeMars R, Pauza CD, Johnson RP, Sette A, Watkins DI. Characterization of the peptide binding motif of a rhesus MHC class I molecule (Mamu-A*01) that binds an immunodominant CTL epitope from simian immunodeficiency virus. J Immunol. 1998;160(12):6062–71. - PubMed
-
- Andrew DP, Rott LS, Kilshaw PJ, Butcher EC. Distribution of alpha 4 beta 7 and alpha E beta 7 integrins on thymocytes, intestinal epithelial lymphocytes and peripheral lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1996;26(4):897–905. - PubMed
-
- Baig J, Levy DB, McKay PF, Schmitz JE, Santra S, Subbramanian RA, Kuroda MJ, Lifton MA, Gorgone DA, Wyatt LS, Moss B, Huang Y, Chakrabarti BK, Xu L, Kong WP, Yang ZY, Mascola JR, Nabel GJ, Carville A, Lackner AA, Veazey RS, Letvin NL. Elicitation of simian immunodeficiency virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in mucosal compartments of rhesus monkeys by systemic vaccination. J Virol. 2002;76(22):11484–90. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Betts MR, Exley B, Price DA, Bansal A, Camacho ZT, Teaberry V, West SM, Ambrozak DR, Tomaras G, Roederer M, Kilby JM, Tartaglia J, Belshe R, Gao F, Douek DC, Weinhold KJ, Koup RA, Goepfert P, Ferrari G. Characterization of functional and phenotypic changes in anti-Gag vaccine-induced T cell responses and their role in protection after HIV-1 infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(12):4512–7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bishop DK, Hinrichs DJ. Adoptive transfer of immunity to Listeria monocytogenes. The influence of in vitro stimulation on lymphocyte subset requirements. J Immunol. 1987;139(6):2005–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

