A neuropsychiatric model of biological and psychological processes in the remission of delusions and auditory hallucinations
- PMID: 16905635
- PMCID: PMC2632542
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbl027
A neuropsychiatric model of biological and psychological processes in the remission of delusions and auditory hallucinations
Abstract
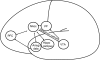
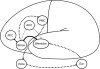
This selective review combines cognitive models and biological models of psychosis into a tentative integrated neuropsychiatric model. The aim of the model is to understand better, how pharmacotherapy and cognitive-behavior therapy come forward as partners in the treatment of psychosis and play complementary and mutually reinforcing roles. The article reviews the dominant models in literature. The focus in this review is on one hand on neural circuits that are involved in cognitive models and on the other hand on cognitive processes and experiences involved in biological models. In this way, a 4-component neuropsychiatric model is tentatively constructed: (1) a biological component that leads to aberrant perceptions and salience of stimuli, (2) a cognitive component that attempts to explain the psychic abnormal events, (3) a mediating component with psychological biases which influences the reasoning process in the direction of the formation of (secondary) delusions, and (4) a component of psychological processes that maintains delusions and prevents the falsification of delusional ideas. Remission consists actually of 2 processes. Biological remission consists of the dampening of mesolimbic dopamine releases with antipsychotic medication and decreases the continuous salient experiences. Psychological remission consists of the reappraisal of primary psychotic experiences. Both forms of remission are partially independent. We expect that a full remission including biological and psychological remission could prevent relapse.
Figures
References
-
- Liddle, PF, Barnes, TR, Morris, D, Haque, S. Three syndromes in chronic schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 1989. ;7119–122. - PubMed
-
- Broome, MR, Woolley, JB, Tabraham, P, et al. What causes the onset of psychosis? Schizophr Res 2005. ;7923–34. - PubMed
-
- Kapur, S. Psychosis as a state of aberrant salience: a framework linking biology, phenomenology, and pharmacology in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2003. ;16013–23. - PubMed
-
- Kapur, S, Mizrahi, R, Li, M. From dopamine to salience to psychosis-linking biology, pharmacology and phenomenology of psychosis. Schizophr Res 2005. ;7959–68. - PubMed
-
- Hohwy, J and Rosenberg, R. Cognitive neuropsychiatry: conceptual, methodological and philosophical perspectives. World J Biol Psychiatry 2005. ;6192–197. - PubMed