Bistable expression of WOR1, a master regulator of white-opaque switching in Candida albicans
- PMID: 16905649
- PMCID: PMC1540355
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0605270103
Bistable expression of WOR1, a master regulator of white-opaque switching in Candida albicans
Abstract
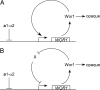
Candida albicans, a commensal organism and a pathogen of humans, can switch stochastically between a white phase and an opaque phase without an intermediate phase. The white and opaque phases have distinct cell shapes and gene expression programs. Once switched, each phase is stable for many cell divisions. White-opaque switching is under a1-alpha2 repression and therefore only happens in a or alpha cells. Mechanisms that control the switching are unknown. Here, we identify Wor1 (white-opaque regulator 1) as a master regulator of white-opaque switching. The deletion of WOR1 blocks opaque cell formation. The ectopic expression of WOR1 converts all cells to stable opaque cells in a or alpha cells. In addition, the ectopic expression of WOR1 in a/alpha cells is sufficient to induce opaque cell formation. Importantly, WOR1 expression displays an all-or-none pattern. It is undetectable in white cells, and it is highly expressed in opaque cells. The ectopic expression of Wor1 induces the transcription of WOR1 from the WOR1 locus, which correlates with the switch to opaque phase. We present genetic evidence for feedback regulation of WOR1 transcription. The feedback regulation explains the bistable and stochastic nature of white-opaque switching.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures

Comment in
-
Single gene control of a complex phenotype hangs in the balance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 22;103(34):12659-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605675103. Epub 2006 Aug 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16908836 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

