Visualizing plant development and gene expression in three dimensions using optical projection tomography
- PMID: 16905654
- PMCID: PMC1560903
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.043042
Visualizing plant development and gene expression in three dimensions using optical projection tomography
Abstract
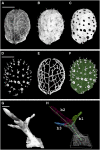
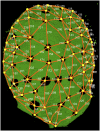
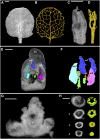
A deeper understanding of the mechanisms that underlie plant growth and development requires quantitative data on three-dimensional (3D) morphology and gene activity at a variety of stages and scales. To address this, we have explored the use of optical projection tomography (OPT) as a method for capturing 3D data from plant specimens. We show that OPT can be conveniently applied to a wide variety of plant material at a range of scales, including seedlings, leaves, flowers, roots, seeds, embryos, and meristems. At the highest resolution, large individual cells can be seen in the context of the surrounding plant structure. For naturally semitransparent structures, such as roots, live 3D imaging using OPT is also possible. 3D domains of gene expression can be visualized using either marker genes, such as beta-glucuronidase, or more directly by whole-mount in situ hybridization. We also describe tools and software that allow the 3D data to be readily quantified and visualized interactively in different ways.
Figures
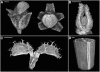
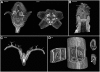

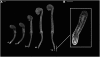
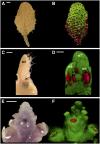
References
-
- Baldock, R.A., et al. (2003). EMAP and EMAGE: A framework for understanding spatially organized data. Neuroinformatics 1 309–325. - PubMed
-
- Blazquez, M.A., Soowal, L.N., Lee, I., and Weigel, D. (1997). LEAFY expression and flower initiation in Arabidopsis. Development 124 3835–3844. - PubMed
-
- Blythe, D. (1998). Advanced Graphics Programming Techniques Using OpenGL. SIGGRAPH 1998 Course. (New York: ACM Press).
-
- Bryson-Richardson, R.J., and Currie, P.D. (2004). Optical projection tomography for spatio-temporal analysis in the zebrafish. Methods Cell Biol. 76 37–50. - PubMed
-
- Coen, E.S., Romero, J.M., Doyle, S., Elliott, R., Murphy, G., and Carpenter, R. (1990). Floricaula: A homeotic gene required for flower development in Antirrhinum majus. Cell 63 1311–1322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

