Metrics for external model evaluation with an application to the population pharmacokinetics of gliclazide
- PMID: 16906454
- PMCID: PMC2124466
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-006-9067-5
Metrics for external model evaluation with an application to the population pharmacokinetics of gliclazide
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this study is to define and illustrate metrics for the external evaluation of a population model.
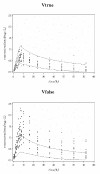
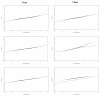
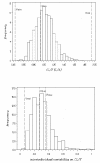
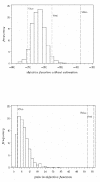
Materials and methods: In this paper, several types of metrics are defined: based on observations (standardized prediction error with or without simulation and normalized prediction distribution error); based on hyperparameters (with or without simulation); based on the likelihood of the model. All the metrics described above are applied to evaluate a model built from two phase II studies of gliclazide. A real phase I dataset and two datasets simulated with the real dataset design are used as external validation datasets to show and compare how metrics are able to detect and explain potential adequacies or inadequacies of the model.
Results: Normalized prediction errors calculated without any approximation, and metrics based on hyperparameters or on objective function have good theoretical properties to be used for external model evaluation and showed satisfactory behaviour in the simulation study.
Conclusions: For external model evaluation, prediction distribution errors are recommended when the aim is to use the model to simulate data. Metrics through hyperparameters should be preferred when the aim is to compare two populations and metrics based on the objective function are useful during the model building process.
Figures


References
-
- Sheiner LB, Steimer JL. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling in drug development. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000;40:67–95. - PubMed
-
- Aarons L, Karlsson MO, Mentre F, Rombout F, Steimer JL, van Peer A. Role of modelling and simulation in Phase I drug development. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2001;13:115–122. - PubMed
-
- Jochemsen R, Laveille C, Breimer DD. Application of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modelling and population approaches to drug development. International J of Pharmaceutical Medicine. 1999;13:243–251.
-
- Holford NH, Kimko HC, Monteleone JP, Peck CC. Simulation of clinical trials. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000;40:209–234. - PubMed
-
- Lesko LJ, Rowland M, Peck CC, Blaschke TF. Optimizing the science of drug development: opportunities for better candidate selection and accelerated evaluation in humans. Pharm Res. 2000;17:1335–1344. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

