Ultraviolet-A (UVA-1) radiation suppresses immunoglobulin production of activated B lymphocytes in vitro
- PMID: 16907923
- PMCID: PMC1809712
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03136.x
Ultraviolet-A (UVA-1) radiation suppresses immunoglobulin production of activated B lymphocytes in vitro
Abstract
Previous studies have shown that low-dose ultraviolet-A (UVA-1) total body irradiations were capable of improving disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). We hypothesized that UVA-1-induced suppression of immunoglobulin production by activated B cells in the dermal capillaries could be (partly) responsible for this effect. Our experiments with donor skin demonstrated that approximately 40% of UVA-1 could penetrate through the epidermis. Irradiation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with 2 J/cm(2) of UVA-1 resulted in 20% cell death. This toxic effect could be prevented totally by preincubation of the cell cultures with catalase. This indicates that the generation of hydrogen peroxide plays a role in UVA-1 cytotoxicity. T cells and B cells appeared to be less susceptible to UVA-1 cytotoxicity than monocytes. With the use of a CD40-CD40L B cell activation method we measured immunoglobulin production after various doses of UVA-1 irradiation (0-2 J/cm(2)). The doses of 2 J/cm(2) caused a significant decrease of IgM, IgG, IgA and IgE production under the conditions of interleukin (IL)-10 or IL-4 (IgE) stimulation. Although UVA-1 can cause apoptosis of B lymphocytes, we show that relatively low doses of UVA-1 radiation also affect the function of these cells. Both effects may be responsible for the observed improvement of disease activity in SLE patients.
Figures


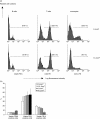
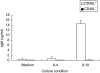
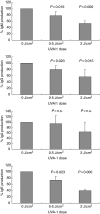
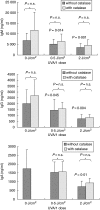
References
-
- Grammer AC, Lipsky PE. CD154–CD40 interactions mediate differentiation to plasma cells in healthy individuals and persons with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1417–29. - PubMed
-
- Gescuk BD, Davis JC., Jr Novel therapeutic agents for systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2002;14:515–21. - PubMed
-
- Wallace DJ. Management of lupus erythematosus: recent insights. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2002;14:212–19. - PubMed
-
- McGrath H, Martinez-Osuna P, Lee FA. Ultraviolet-A1 (340–400 nm) irradiation therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 1996;5:269–74. - PubMed
-
- McGrath H., Jr Ultraviolet-A1 irradiation decreases clinical disease activity and autoantibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1994;12:129–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

