NMDA receptor-nitric oxide transmission mediates neuronal iron homeostasis via the GTPase Dexras1
- PMID: 16908409
- PMCID: PMC3150500
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.07.011
NMDA receptor-nitric oxide transmission mediates neuronal iron homeostasis via the GTPase Dexras1
Abstract
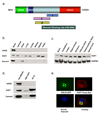
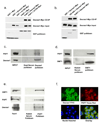
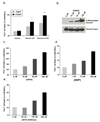
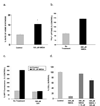
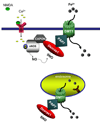
Dexras1 is a 30 kDa G protein in the Ras subfamily whose discovery was based on its pronounced inducibility by the glucocorticoid dexamethasone. It binds to neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) via the adaptor protein CAPON, eliciting S-nitrosylation and activation of Dexras1. We report that Dexras1 binds to the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor-associated protein (PAP7), a protein of unknown function that binds to cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. PAP7 in turn binds to the divalent metal transporter (DMT1), an iron import channel. We have identified a signaling cascade in neurons whereby stimulation of NMDA receptors activates nNOS, leading to S-nitrosylation and activation of Dexras1, which, via PAP7 and DMT1, physiologically induces iron uptake. As selective iron chelation prevents NMDA neurotoxicity in cortical cultures, the NMDA-NO-Dexras1-PAP7-DMT1-iron uptake signaling cascade also appears to mediate NMDA neurotoxicity.
Figures



References
-
- Blumer JB, Cismowski MJ, Sato M, Lanier SM. AGS proteins: receptor-independent activators of G-protein signaling. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2005;26:470–476. - PubMed
-
- Bredt DS, Snyder SH. Nitric oxide: a physiologic messenger molecule. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994;63:175–195. - PubMed
-
- Brenman JE, Chao DS, Gee SH, McGee AW, Craven SE, Santillano DR, Wu Z, Huang F, Xia H, Peters MF, Froehner SC, Bredt DS. Interaction of nitric oxide synthase with the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 and alpha1-syntrophin mediated by PDZ domains. Cell. 1996;84:757–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

