Syntenin-1 is a new component of tetraspanin-enriched microdomains: mechanisms and consequences of the interaction of syntenin-1 with CD63
- PMID: 16908530
- PMCID: PMC1636879
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00849-06
Syntenin-1 is a new component of tetraspanin-enriched microdomains: mechanisms and consequences of the interaction of syntenin-1 with CD63
Abstract
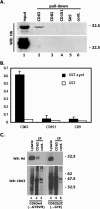
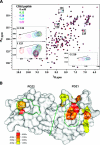
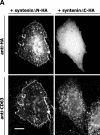
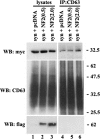
Tetraspanins are clustered in specific microdomains (named tetraspanin-enriched microdomains, or TERM) in the plasma membrane and regulate the functions of associated transmembrane receptors, including integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases. We have identified syntenin-1, a PDZ domain-containing protein, as a new component of TERM and show that syntenin-1 specifically interacts with the tetraspanin CD63. Detailed biochemical and heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) studies have demonstrated that the interaction is mediated by the C-terminal cytoplasmic region of the tetraspanin and the PDZ domains of syntenin-1. Upon interaction, NMR chemical shift perturbations were predominantly localized to residues around the binding pocket of PDZ1, indicating a specific mode of recognition of the cytoplasmic tail of CD63. In addition, the C terminus of syntenin-1 has a stabilizing role in the CD63-syntenin-1 association, as deletion of the last 17 amino acids abolished the interaction. The CD63-syntenin-1 complex is abundant on the plasma membrane, and the elevated expression of the wild-type syntenin-1 slows down constitutive internalization of the tetraspanin. Furthermore, internalization of CD63 was completely blocked in cells expressing a syntenin-1 mutant lacking the first 100 amino acids. Previous results have shown that CD63 is internalized via AP-2-dependent mechanisms. Hence, our data indicate that syntenin-1 can counteract the AP-2-dependent internalization and identify this tandem PDZ protein as a new regulator of endocytosis.
Figures





References
-
- Adey, N. B., L. Huang, P. A. Ormonde, M. L. Baumgard, R. Pero, D. V. Byreddy, S. V. Tavtigian, and P. L. Bartel. 2000. Threonine phosphorylation of the MMAC1/PTEN PDZ binding domain both inhibits and stimulates PDZ binding. Cancer Res. 60:35-37. - PubMed
-
- Amezcua, C. A., S. M. Harper, J. Rutter, and K. H. Gardner. 2002. Structure and interactions of PAS kinase N-terminal PAS domain: model for intramolecular kinase regulation. Structure 10:1349-1361. - PubMed
-
- Berditchevski, F. 2001. Complexes of tetraspanins with integrins: more than meets the eye. J. Cell Sci. 115:4143-4151. - PubMed
-
- Berditchevski, F., G. Bazzoni, and M. E. Hemler. 1995. Specific association of CD63 with the VLA-3 and VLA-6 integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 270:17784-17790. - PubMed
-
- Berditchevski, F., S. Chang, J. Bodorova, and M. E. Hemler. 1997. Generation of monoclonal antibodies to integrin-associated proteins. Evidence that alpha3beta1 complexes with EMMPRIN/basigin/OX47/M6. J. Biol. Chem. 272:29174-29180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
