Oligonucleotide microarray analysis of genomic imbalance in children with mental retardation
- PMID: 16909388
- PMCID: PMC1559542
- DOI: 10.1086/507471
Oligonucleotide microarray analysis of genomic imbalance in children with mental retardation
Erratum in
- Am J Hum Genet. 2006 Dec;79(6):1135. Armstrong, Linlea [added]
Abstract
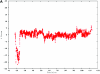
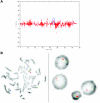
The cause of mental retardation in one-third to one-half of all affected individuals is unknown. Microscopically detectable chromosomal abnormalities are the most frequently recognized cause, but gain or loss of chromosomal segments that are too small to be seen by conventional cytogenetic analysis has been found to be another important cause. Array-based methods offer a practical means of performing a high-resolution survey of the entire genome for submicroscopic copy-number variants. We studied 100 children with idiopathic mental retardation and normal results of standard chromosomal analysis, by use of whole-genome sampling analysis with Affymetrix GeneChip Human Mapping 100K arrays. We found de novo deletions as small as 178 kb in eight cases, de novo duplications as small as 1.1 Mb in two cases, and unsuspected mosaic trisomy 9 in another case. This technology can detect at least twice as many potentially pathogenic de novo copy-number variants as conventional cytogenetic analysis can in people with mental retardation.
Figures
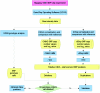
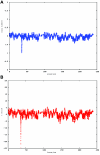
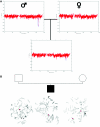
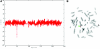













References
Web Resources
-
- Affymetrix GeneChip Human Mapping 100K Assay Manual, http://www.affymetrix.com/support/downloads/manuals/100k_manual.pdf - PMC - PubMed
-
- Database of Genomic Variants, http://projects.tcag.ca/variation/
-
- GeneChip DNA Analysis Software (GDAS) Version 3.0, http://www.affymetrix.com/Auth/support/downloads/manuals/gdas_manual.zip
References
-
- Roeleveld N, Zielhuis G, Gabreels F (1997) The prevalence of mental retardation: a critical review of recent literature. Dev Med Child Neurol 39:125–132 - PubMed
-
- Pope A, Tarlov A (1991) Disability in America: toward a national agenda for prevention. Institute of Medicine, Washington, DC
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

