Preventing autoimmune arthritis using antigen-specific immature dendritic cells: a novel tolerogenic vaccine
- PMID: 16911769
- PMCID: PMC1779442
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2031
Preventing autoimmune arthritis using antigen-specific immature dendritic cells: a novel tolerogenic vaccine
Abstract
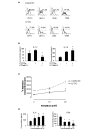
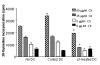
Conventional treatments for autoimmune diseases have relied heavily on nonspecific immune suppressants, which possess a variety of adverse effects without inhibiting the autoimmune process in a specific manner. In the present study we demonstrate the effectiveness of antigen-specific, maturation-resistant, tolerogenic dendritic cells (DC) in suppressing collagen-induced arthritis, a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment of DC progenitors with the NF-kappaB inhibiting agent LF 15-0195 (LF) resulted in a population of tolerogenic DC that are characterized by low expression of MHC class II, CD40, and CD86 molecules, as well as by poor allostimulatory capacity in a mixed leukocyte reaction. Administering LF-treated DC pulsed with keyhole limpet hemocyanin antigen to naïve mice resulted hyporesponsiveness specific for this antigen. Furthermore, administration of LF-treated DC to mice with collagen-induced arthritis resulted in an improved clinical score, in an inhibited antigen-specific T-cell response, and in reduced antibody response to the collagen. The efficacy of LF-treated DC in preventing arthritis was substantiated by histological examination, which revealed a significant decrease in inflammatory cell infiltration in the joints. In conclusion, we demonstrate that in vitro-generated antigen-specific immature DC may have important potential as a tolerogenic vaccine for the treatment of autoimmune arthritis.
Figures
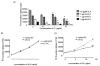
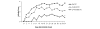

Similar articles
-
Antigen-induced, tolerogenic CD11c+,CD11b+ dendritic cells are abundant in Peyer's patches during the induction of oral tolerance to type II collagen and suppress experimental collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Mar;54(3):887-98. doi: 10.1002/art.21647. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16508971
-
Longterm protection of mice against collagen-induced arthritis after short-term LF 15-0195 treatment: modulation of B and T lymphocyte activation.J Rheumatol. 2003 May;30(5):918-25. J Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 12734883
-
Oral administration of type-II collagen peptide 250-270 suppresses specific cellular and humoral immune response in collagen-induced arthritis.Clin Immunol. 2007 Jan;122(1):75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.08.004. Epub 2006 Oct 11. Clin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17045846
-
Induction of tolerogenic dendritic cells by vitamin D receptor agonists.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(188):251-73. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-71029-5_12. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19031030 Review.
-
Regulation of dendritic cell differentiation by vasoactive intestinal peptide: therapeutic applications on autoimmunity and transplantation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Nov;1088:187-94. doi: 10.1196/annals.1366.004. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17192565 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Hyporesponsive CD4(+) T Cells in Autoimmunity.Front Immunol. 2015 Sep 22;6:488. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00488. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26441992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome removal as a therapeutic adjuvant in cancer.J Transl Med. 2012 Jun 27;10:134. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-134. J Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22738135 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic cells loaded with FK506 kill T cells in an antigen-specific manner and prevent autoimmunity in vivo.Elife. 2013 Feb 5;2:e00105. doi: 10.7554/eLife.00105. Elife. 2013. PMID: 23390586 Free PMC article.
-
Tolerogenic dendritic cells and rheumatoid arthritis: current status and perspectives.Rheumatol Int. 2012 Apr;32(4):837-44. doi: 10.1007/s00296-011-2133-2. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Rheumatol Int. 2012. PMID: 21904923 Review.
-
Tolerogenic dendritic cells are efficiently generated using minocycline and dexamethasone.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 8;7(1):15087. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15569-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29118423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Heusch M, Oldenhove G, Urbain J, Thielemans K, Maliszewski C, Leo O, Moser M. Depending on their maturation state, splenic dendritic cells induce the differentiation of CD4(+) T lymphocytes into memory and/or effector cells in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:1861–1869. doi: 10.1002/eji.200424878. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

