Plasma osteopontin levels in patients with head and neck cancer and cervix cancer are critically dependent on the choice of ELISA system
- PMID: 16911785
- PMCID: PMC1564036
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-207
Plasma osteopontin levels in patients with head and neck cancer and cervix cancer are critically dependent on the choice of ELISA system
Abstract
Background: The tumor-associated glycoprotein osteopontin (OPN) is discussed as a plasma surrogate marker of tumor hypoxia and as an indicator of the presence of pleural mesothelioma in asbestos-exposed individuals. The clinical introduction of plasma OPN measurements requires the availability of a reliable enzyme-linked immunosorbence assay (ELISA).
Methods: We compared previously described and currently available ELISA systems on 88 archival plasma samples obtained from patients with head and neck or cervix cancer between 20 days before and 171 after the start of radiotherapy.
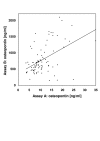
Results: Median (range) plasma OPN levels were 667 (148.8-2095) ng/ml and 9.8 (3.5-189.5) ng/ml for a previously described and a newly marketed assay, respectively. Although results for different assays were significantly correlated (r = 0.38, p < 0.05, Spearman rank test), between-assay factors ranged from 2.0 to 217.9 (median 74.6) in individual patients. OPN levels in cervix cancer patients were comparable to those of head and neck cancer patients.
Conclusion: Commercially available OPN ELISA systems produce different absolute plasma OPN levels, compromising a comparison of individual patient data with published results. However, different assays appear to have a similar capacity to rank patients according to plasma OPN level. A review of literature data suggests that plasma OPN levels measured even with identical ELISA systems can only be compared with caution.
Figures
References
-
- Le QT, Sutphin PD, Raychaudhuri S, Yu SC, Terris DJ, Lin HS, Lum B, Pinto HA, Koong AC, Giaccia AJ. Identification of osteopontin as a prognostic plasma marker for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Overgaard J, Eriksen JG, Nordsmark M, Alsner J, Horsman MR, Danish Head and Neck Cancer Study Group Plasma osteopontin, hypoxia, and response to the hypoxia sensitiser nimorazole in radiotherapy of head and neck cancer: results from the DAHANCA 5 randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6:757–764. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(05)70292-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

