Ultrasonic tissue characterization of vulnerable carotid plaque: correlation between videodensitometric method and histological examination
- PMID: 16914059
- PMCID: PMC1562449
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-4-32
Ultrasonic tissue characterization of vulnerable carotid plaque: correlation between videodensitometric method and histological examination
Abstract
Background: To establish the correlation between quantitative analysis based on B-mode ultrasound images of vulnerable carotid plaque and histological examination of the surgically removed plaque, on the basis of a videodensitometric digital texture characterization.
Methods: Twenty-five patients (18 males, mean age 67 +/- 6.9 years) admitted for carotid endarterectomy for extracranial high-grade internal carotid artery stenosis (> or = 70% luminal narrowing) underwent to quantitative ultrasonic tissue characterization of carotid plaque before surgery. A computer software (Carotid Plaque Analysis Software) was developed to perform the videodensitometric analysis. The patients were divided into 2 groups according to symptomatology (group I, 15 symptomatic patients; and group II, 10 patients asymptomatic). Tissue specimens were analysed for lipid, fibromuscular tissue and calcium.
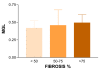
Results: The first order statistic parameter mean gray level was able to distinguish the groups I and II (p = 0.04). The second order parameter energy also was able to distinguish the groups (p = 0,02). A histological correlation showed a tendency of mean gray level to have progressively greater values from specimens with < 50% to > 75% of fibrosis.
Conclusion: Videodensitometric computer analysis of scan images may be used to identify vulnerable and potentially unstable lipid-rich carotid plaques, which are less echogenic in density than stable or asymptomatic, more densely fibrotic plaques.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Videodensitometric analysis of advanced carotid plaque: correlation with MMP-9 and TIMP-1 expression.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2011 Sep 18;9:24. doi: 10.1186/1476-7120-9-24. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2011. PMID: 21923935 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
In vivo ultrasonic parametric imaging of carotid atherosclerotic plaque by videodensitometric technique.Angiology. 1995 Aug;46(8):663-72. doi: 10.1177/000331979504600804. Angiology. 1995. PMID: 7639412
-
Pixel distribution analysis of B-mode ultrasound scan images predicts histologic features of atherosclerotic carotid plaques.J Vasc Surg. 2002 Jun;35(6):1210-7. doi: 10.1067/mva.2002.122888. J Vasc Surg. 2002. PMID: 12042733
-
Comparison of lipid-rich necrotic core size in symptomatic and asymptomatic carotid atherosclerotic plaque: Initial results.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008 Jun;27(6):1356-61. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21359. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008. PMID: 18504755 Clinical Trial.
-
Gender-associated differences in plaque phenotype of patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy.J Vasc Surg. 2007 Feb;45(2):289-96; discussion 296-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2006.09.051. J Vasc Surg. 2007. PMID: 17264005
Cited by
-
The Accuracy of Noninvasive Imaging Techniques in Diagnosis of Carotid Plaque Morphology.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2015 Jun 15;3(2):224-30. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2015.039. Epub 2015 Mar 27. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 27275225 Free PMC article.
-
Videodensitometric analysis of advanced carotid plaque: correlation with MMP-9 and TIMP-1 expression.Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2011 Sep 18;9:24. doi: 10.1186/1476-7120-9-24. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2011. PMID: 21923935 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasound tissue characterization of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 May 5;16(5):10121-33. doi: 10.3390/ijms160510121. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25950760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation between calcium, water contents and ultrasonographic appearance of atherosclerotic lesions of carotid artery lesions.Transl Neurosci. 2020 Aug 24;11(1):269-276. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2020-0115. eCollection 2020. Transl Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33335767 Free PMC article.
-
Histological composition and progression of carotid plaque.Thromb J. 2007 Feb 26;5:4. doi: 10.1186/1477-9560-5-4. Thromb J. 2007. PMID: 17324272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnett HJM, Taylor DW, Eliasziw M, Fox AJ, Ferguson GG, Haynes RB, Rankin RN, Clagett GP, Hachinski VC, Sackett DL, Thorpe KE, Math M, Meldrum HE. Benefit of carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic moderate or severe stenosis. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1415–1425. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199811123392002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial collaborators Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high – grade carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:445–453. - PubMed
-
- Barnett HJM, Meldrum HE, Eliasziw M. The dilemma of surgical treatment for patients with asymptomatic carotid disease. Ann Intern Med. 1995;123:723–725. - PubMed
-
- Wilhjelm JE, Grønholdt MLM, Wiebe B, Jespersen SK, Hansen LK, Sillesen H. Quantitative analysis of ultrasound B-mode images of carotid atherosclerotic plaque: correlation with visual classification and histological examination. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 1998;17:910–922. doi: 10.1109/42.746624. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

