Valosin-containing protein (p97) is a regulator of endoplasmic reticulum stress and of the degradation of N-end rule and ubiquitin-fusion degradation pathway substrates in mammalian cells
- PMID: 16914519
- PMCID: PMC1635394
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-05-0432
Valosin-containing protein (p97) is a regulator of endoplasmic reticulum stress and of the degradation of N-end rule and ubiquitin-fusion degradation pathway substrates in mammalian cells
Abstract
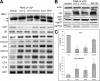
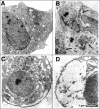
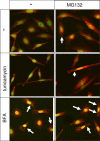
Valosin-containing protein (VCP; p97; cdc48 in yeast) is a hexameric ATPase of the AAA family (ATPases with multiple cellular activities) involved in multiple cellular functions, including degradation of proteins by the ubiquitin (Ub)-proteasome system (UPS). We examined the consequences of the reduction of VCP levels after RNA interference (RNAi) of VCP. A new stringent method of microarray analysis demonstrated that only four transcripts were nonspecifically affected by RNAi, whereas approximately 30 transcripts were affected in response to reduced VCP levels in a sequence-independent manner. These transcripts encoded proteins involved in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, apoptosis, and amino acid starvation. RNAi of VCP promoted the unfolded protein response, without eliciting a cytosolic stress response. RNAi of VCP inhibited the degradation of R-GFP (green fluorescent protein) and Ub-(G76V)-GFP, two cytoplasmic reporter proteins degraded by the UPS, and of alpha chain of the T-cell receptor, an established substrate of the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway. Surprisingly, RNAi of VCP had no detectable effect on the degradation of two other ERAD substrates, alpha1-antitrypsin and deltaCD3. These results indicate that VCP is required for maintenance of normal ER structure and function and mediates the degradation of some proteins via the UPS, but is dispensable for the UPS-dependent degradation of some ERAD substrates.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Destabilization of the VCP-Ufd1-Npl4 complex is associated with decreased levels of ERAD substrates.Exp Cell Res. 2006 Sep 10;312(15):2921-32. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.05.013. Epub 2006 Jun 6. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16822501
-
Identification of SVIP as an endogenous inhibitor of endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 23;282(47):33908-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704446200. Epub 2007 Sep 14. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17872946
-
AAA ATPase p97/valosin-containing protein interacts with gp78, a ubiquitin ligase for endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation.J Biol Chem. 2004 Oct 29;279(44):45676-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409034200. Epub 2004 Aug 24. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15331598
-
Clipping or Extracting: Two Ways to Membrane Protein Degradation.Trends Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;25(10):611-622. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.07.003. Trends Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26410407 Review.
-
VCP/p97/Cdc48, A Linking of Protein Homeostasis and Cancer Therapy.Curr Mol Med. 2017;17(9):608-618. doi: 10.2174/1566524018666180308111238. Curr Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 29521227 Review.
Cited by
-
Valosin-containing protein regulates the proteasome-mediated degradation of DNA-PKcs in glioma cells.Cell Death Dis. 2013 May 30;4(5):e647. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.171. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23722536 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal-specific overexpression of a mutant valosin-containing protein associated with IBMPFD promotes aberrant ubiquitin and TDP-43 accumulation and cognitive dysfunction in transgenic mice.Am J Pathol. 2013 Aug;183(2):504-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.04.014. Epub 2013 Jun 5. Am J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23747512 Free PMC article.
-
Control of cellular GADD34 levels by the 26S proteasome.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;28(23):6989-7000. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00724-08. Epub 2008 Sep 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18794359 Free PMC article.
-
HSC70 and HSP90 chaperones perform complementary roles in translocation of the cholera toxin A1 subunit from the endoplasmic reticulum to the cytosol.J Biol Chem. 2019 Aug 9;294(32):12122-12131. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008568. Epub 2019 Jun 20. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31221799 Free PMC article.
-
Improving drug discovery with high-content phenotypic screens by systematic selection of reporter cell lines.Nat Biotechnol. 2016 Jan;34(1):70-77. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3419. Epub 2015 Dec 14. Nat Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26655497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arai H. Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002;68–69:83–94. - PubMed
-
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986;234:179–186. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Nun S. The role of p97/Cdc48p in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation: from the immune system to yeast. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005;300:95–125. - PubMed
-
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
-
- Chopra S., Wallace H. M. Induction of spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase in human cancer cells in response to increased production of reactive oxygen species. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998;55:1119–1123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

