Heregulin-dependent delay in mitotic progression requires HER4 and BRCA1
- PMID: 16914727
- PMCID: PMC1592831
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01950-05
Heregulin-dependent delay in mitotic progression requires HER4 and BRCA1
Abstract
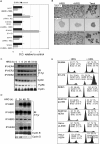
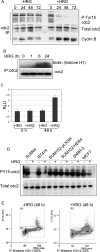
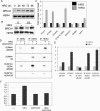
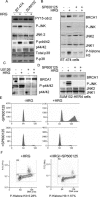
HER4 expression in human breast cancers correlates with a positive prognosis. While heregulin inhibits the growth of HER4-positive breast cancer cells, it does so by undefined mechanisms. We demonstrate that heregulin-induced HER4 activity inhibits cell proliferation and delays G(2)/M progression of breast cancer cells. While investigating pathways of G(2)/M delay, we noted that heregulin increased the expression of BRCA1 in a HER4-dependent, HER2-independent manner. Induction of BRCA1 by HER4 occurred independently of the cell cycle. Moreover, BRCA1 expression was elevated in HER4-postive human breast cancer specimens. Heregulin stimulated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and pharmacologic inhibition of JNK impaired heregulin-enhanced expression of BRCA1 and mitotic delay; inhibition of Erk1/2 did not. Knockdown of BRCA1 with small interfering RNA in a human breast cancer cell line interfered with HER4-mediated mitotic delay. Heregulin/HER4-dependent mitotic delay was examined further with an isogenic pair of mouse mammary epithelial cells (MECs) derived from mice harboring homozygous LoxP sites flanking exon 11 of BRCA1, such that one cell line expressed BRCA1 while the other cell line, after Cre-mediated excision, did not. BRCA1-positive MECs displayed heregulin-dependent mitotic delay; however, the isogenic BRCA1-negative MECs did not. These results suggest that heregulin-mediated growth inhibition in HER4-postive breast cancer cells requires BRCA1.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Her4 mediates ligand-dependent antiproliferative and differentiation responses in human breast cancer cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jul;21(13):4265-75. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.13.4265-4275.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11390655 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of BRCA1 leads to an increase in epidermal growth factor receptor expression in mammary epithelial cells, and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition prevents estrogen receptor-negative cancers in BRCA1-mutant mice.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Mar 11;13(2):R30. doi: 10.1186/bcr2850. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21396117 Free PMC article.
-
Heregulin activation of extracellular acidification in mammary carcinoma cells is associated with expression of HER2 and HER3.J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 22;270(38):22608-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.38.22608. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7673253
-
The significance of heregulin in breast cancer tumor progression and drug resistance.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996;38(1):57-66. doi: 10.1007/BF01803784. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996. PMID: 8825123 Review.
-
HER4 intracellular domain (4ICD) activity in the developing mammary gland and breast cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008 Jun;13(2):247-58. doi: 10.1007/s10911-008-9076-6. Epub 2008 May 13. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 18473151 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biasing human epidermal growth factor receptor 4 (HER4) tyrosine kinase signaling with antibodies: Induction of cell death by antibody-dependent HER4 intracellular domain trafficking.Cancer Sci. 2020 Jul;111(7):2508-2525. doi: 10.1111/cas.14458. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 32415868 Free PMC article.
-
ErbB4/HER4: role in mammary gland development, differentiation and growth inhibition.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008 Jun;13(2):235-46. doi: 10.1007/s10911-008-9080-x. Epub 2008 Apr 25. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 18437540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive review of heregulins, HER3, and HER4 as potential therapeutic targets in cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 13;8(51):89284-89306. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18467. eCollection 2017 Oct 24. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29179520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Portrait of WWP1: the current state in human cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jan 30;12:1516613. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1516613. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39949609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 4 (HER4) is a favorable prognostic marker of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 22;7(47):76693-76703. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12485. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27736797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abd El-Rehim, D. M., S. E. Pinder, C. E. Paish, J. A. Bell, R. S. Rampaul, R. W. Blamey, J. F. Robertson, R. I. Nicholson, and I. O. Ellis. 2004. Expression and co-expression of the members of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) family in invasive breast carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 91:1532-1542. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alimandi, M., A. Romano, M. C. Curia, R. Muraro, P. Fedi, S. A. Aaronson, P. P. Di Fiore, and M. H. Kraus. 1995. Cooperative signaling of ErbB3 and ErbB2 in neoplastic transformation and human mammary carcinomas. Oncogene 10:1813-1821. - PubMed
-
- Altiok, S., D. Batt, N. Altiok, A. Papautsky, J. Downward, T. M. Roberts, and H. Avraham. 1999. Heregulin induces phosphorylation of BRCA1 through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274:32274-32278. - PubMed
-
- Arasada, R. R., and G. Carpenter. 2005. Secretase-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of Mdm2 by the ErbB-4 intracellular domain fragment. J. Biol. Chem. 280:30783-30787. - PubMed
-
- Bobrow, L. G., R. R. Millis, L. C. Happerfield, and W. J. Gullick. 1997. c-erbB-3 protein expression in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Eur. J. Cancer 33:1846-1850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
