The role of infection and comorbidity: Factors that influence disparities in sepsis
- PMID: 16915108
- PMCID: PMC3926300
- DOI: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000239114.50519.0E
The role of infection and comorbidity: Factors that influence disparities in sepsis
Abstract
Objective: Large healthcare disparities exist in the incidence of sepsis based on both race and gender. We sought to determine factors that may influence the occurrence of these healthcare disparities, with respect to the source of infection, causal organisms, and chronic comorbid medical conditions.
Design: Historical cohort study.
Setting: U.S. acute care hospitals from 1979 to 2003.
Patients: Hospitalized patients with a diagnosis of sepsis were identified from the National Hospital Discharge Survey per codes of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9CM). Chronic comorbid medical conditions and the source and type of infection were characterized by corresponding ICD-9CM diagnoses.
Interventions: None.
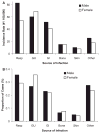
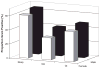
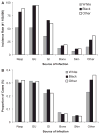
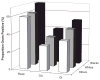
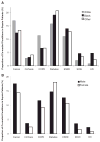
Measurements and main results: Sepsis incidence rates are mean cases per 100,000 after age adjustment to the 2000 U.S. Census. Males and nonwhite races were confirmed at increased risk for sepsis. Both proportional source distribution and incidence rates favored respiratory sources of sepsis in males (36% vs. 29%, p < .01) and genitourinary sources in females (35% vs. 27%, p < .01). Incidence rates for all common sources of sepsis were greater in nonwhite races, but proportional source distribution was approximately equal. After stratification by the source of infection, males (proportionate ratio 1.16, 95% confidence interval 1.04-1.29) and black persons (proportionate ratio 1.25, 95% confidence interval 1.18-1.32) remained more likely to have Gram-positive infections. Chronic comorbid conditions that alter immune function (chronic renal failure, diabetes mellitus, HIV, alcohol abuse) were more common in nonwhite sepsis patients, and cumulative comorbidities were associated with greater acute organ dysfunction. Compared with white sepsis patients, nonwhite sepsis patients had longer hospital length of stay (2.0 days, 95% confidence interval 1.9-2.1) and were less likely to be discharged to another medical facility (30% whites, 25% blacks, 18% other races). Case-fatality rates were not significantly different across racial and gender groups.
Conclusions: Healthcare disparities exist in the incidence of sepsis within all major sources of infection, and males and blacks have greater frequency of Gram-positive infections independent of the infection source. The differential distribution of specific chronic comorbid medical conditions may contribute to these disparities. Large cohort and administrative studies are required to confirm discrete root causes of sepsis disparities.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Martin has disclosed that he was a consultant for GlaxoSmithKline (2004–2005), Pfizer (2004–2005), OrthBiotech (2005), and Dey (2005); he also received honoraria and grants from Pfizer (2005) and GlaxoSmithKline (2004–2005). The remaining authors have not disclosed any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, et al. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest. 1992;101:1644–1655. - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, et al. The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1546–1554. - PubMed
-
- Rangel-Frausto MS, Pittet D, Costigan M, et al. The natural history of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). A prospective study. JAMA. 1995;273:117–123. - PubMed
-
- Brun-Buisson C, Doyon F, Carlet J, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of severe sepsis and septic shock in adults. A multicenter prospective study in intensive care units. JAMA. 1995;274:968–974. - PubMed
-
- Sands KE, Bates DW, Lanken PN, et al. Epidemiology of sepsis syndrome in 8 academic medical centers. Academic Medical Center Consortium Sepsis Project Working Group. JAMA. 1997;278:234–240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

