Antifertility effect of aqueous and ethanol extracts of the leaves and roots of Asparagus africanus in rats
- PMID: 16916296
- PMCID: PMC2567240
- DOI: 10.5555/afhs.2006.6.2.81
Antifertility effect of aqueous and ethanol extracts of the leaves and roots of Asparagus africanus in rats
Abstract
Background: Asparagus africanus is claimed to have use in reproductive related health problems in some areas of Ethiopia.
Objective: To study the potential antifertility effect of the aqueous and ethanol extracts of the leaves and roots of Asparagus africanus in rats.
Methods: Water and ethanol extracts were given by gavages to rats in the in vivo test at a dose of 300 mg/kg of body weight, and rat uterine tissue were used for the in vitro test at different concentrations.
Results: The aqueous extracts of the leaves and the roots showed an anti-implantation activity of 70% and 77%, respectively, while the ethanol extracts of the leaves and roots showed 48% and 61%, respectively. The antifertility activities of the aqueous and ethanol extracts were 40% (for leaves), 60% (for roots) and 20% (for leaves), 40% (for roots), respectively. All the extracts have resulted in significant (P< 0.05) reduction in the number of implants as compared with their respective controls. Each extract potentiated acetylcholine induced uterine contractions in a concentration dependent manner significantly (P< 0.05).
Conclusion: The results obtained in this study suggest that the leaves and roots of this plant may possess hormonal properties that can modulate the reproductive function of the experimental rats.
Figures
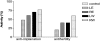

Similar articles
-
Anti-diarrhoeal potential of Asparagus racemosus wild root extracts in laboratory animals.J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2005 Feb 25;8(1):39-46. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2005. PMID: 15946596
-
Antifertility effect of hydroalcoholic leaves extract of Michelia champaca L.: an ethnomedicine used by Bhatra women in Chhattisgarh state of India.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jun 3;147(3):671-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.03.003. Epub 2013 Mar 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23501154
-
Antifertility activity of Artemisia vulgaris leaves on female Wistar rats.Chin J Nat Med. 2014 Mar;12(3):180-5. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(14)60030-3. Chin J Nat Med. 2014. PMID: 24702803
-
Antifertility and profertility effects of the leaves and seeds of fluted pumpkin: Sperm quality, hormonal effects and histomorphological changes in the testes of experimental animal models.J Integr Med. 2021 Mar;19(2):104-110. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2021.01.007. Epub 2021 Jan 14. J Integr Med. 2021. PMID: 33518482 Review.
-
Asparagus racemosus--an update.Indian J Med Sci. 2003 Sep;57(9):408-14. Indian J Med Sci. 2003. PMID: 14515032 Review.
Cited by
-
African Health Sciences. Editor's choice.Afr Health Sci. 2006 Jun;6(2):67. doi: 10.5555/afhs.2006.6.2.67. Afr Health Sci. 2006. PMID: 16916292 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Antidiabetic Indian plants: a good source of potent amylase inhibitors.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:810207. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nen040. Epub 2011 May 2. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. PMID: 18955350 Free PMC article.
-
Nephroprotective Effect of Asparagus africanus Lam. Root Extract against Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Swiss Albino Mice.J Toxicol. 2022 Apr 21;2022:8440019. doi: 10.1155/2022/8440019. eCollection 2022. J Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35495873 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicological study of the butanol fractionated root extract of Asparagus africanus Lam., on some blood parameter and histopathology of liver and kidney in mice.BMC Res Notes. 2016 Jan 27;9:49. doi: 10.1186/s13104-016-1861-5. BMC Res Notes. 2016. PMID: 26817697 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Mechanism of Sarsasapogenin in Treating Precocious Puberty by Regulating the HPG Axis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Aug 5;2020:1978043. doi: 10.1155/2020/1978043. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32831859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Demissew S. Asparagaceae. In: Edward S, Demissew S, Hedberg I, editors. Flora of Ethiopia and Eritrea. Vol. 6. 1997. pp. 67–69.
-
- Kokowaro J O. Asparagus africanus. Medicinal plants of East Africa. 1976:239.
-
- Mungai G M. Some medicinal plants of Amboseli National Park and their uses. Conservation and utilization of indigenous medicinal plants and wild relatives of food crops. 1997:53–56.
-
- Gashaw M. Walia. Vol. 18. 1991. The use and value of wild plants to the people of Bale; pp. 21–28.
-
- Debella A, Haslinger E, Kunert O, Michl G, Abebe Dawit. Steroidal saponins from Asparagus africanus. Phytochemistry. 1999;51:1066–1075. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
