Raf kinase inhibitory protein regulates aurora B kinase and the spindle checkpoint
- PMID: 16916643
- PMCID: PMC1626587
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.07.015
Raf kinase inhibitory protein regulates aurora B kinase and the spindle checkpoint
Abstract
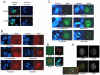
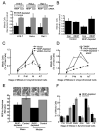
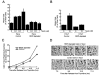
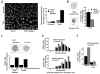
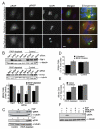
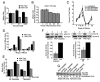
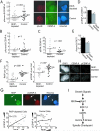
Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP or PEBP) is an inhibitor of the Raf/MEK/MAP kinase signaling cascade and a suppressor of cancer metastasis. We now show that RKIP associates with centrosomes and kinetochores and regulates the spindle checkpoint in mammalian cells. RKIP depletion causes decreases in the mitotic index, the number of metaphase cells, and traversal times from nuclear envelope breakdown to anaphase, and an override of mitotic checkpoints induced by spindle poisons. Raf-1 depletion or MEK inhibition reverses the reduction in the mitotic index, whereas hyperactivation of Raf mimics the RKIP-depletion phenotype. Finally, RKIP depletion or Raf hyperactivation reduces kinetochore localization and kinase activity of Aurora B, a regulator of the spindle checkpoint. These results indicate that RKIP regulates Aurora B kinase and the spindle checkpoint via the Raf-1/MEK/ERK cascade and demonstrate that small changes in the MAP kinase (MAPK) pathway can profoundly impact the fidelity of the cell cycle.
Figures
References
-
- Bharadwaj R, Yu H. The spindle checkpoint, aneuploidy, and cancer. Oncogene. 2004;23:2016–2027. - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee D, Bai Y, Wang Z, Beach S, Mott S, Roy R, Braastad C, Sun Y, Mukhopadhyay A, Aggarwal BB, et al. RKIP sensitizes prostate and breast cancer cells to drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:17515–17523. - PubMed
-
- Corbit KC, Trakul N, Eves EM, Diaz B, Marshall M, Rosner MR. Activation of Raf-1 Signaling by Protein Kinase C through a Mechanism Involving Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:13061–13068. - PubMed
-
- Dhillon AS, Kolch W. Untying the regulation of the Raf-1 kinase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2002;404:3–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

