Transcriptome profiling reveals the importance of plasmid pSymB for osmoadaptation of Sinorhizobium meliloti
- PMID: 16916894
- PMCID: PMC1636257
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00719-06
Transcriptome profiling reveals the importance of plasmid pSymB for osmoadaptation of Sinorhizobium meliloti
Abstract
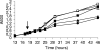
In this work, DNA microarrays were used to investigate genome-wide transcriptional responses of Sinorhizobium meliloti to a sudden increase in external osmolarity elicited by addition of either NaCl or sucrose to exponentially growing cultures. A time course of the response within the first 4 h after the osmotic shock was established. We found that there was a general redundancy in the differentially expressed genes after NaCl or sucrose addition. Both kinds of stress resulted in induction of a large number of genes having unknown functions and in repression of many genes coding for proteins with known functions. There was a strong replicon bias in the pattern of the osmotic stress response; whereas 64% of the upregulated genes had a plasmid localization, 85% of the downregulated genes were chromosomal. Among the pSymB osmoresponsive genes, 83% were upregulated, suggesting the importance of this plasmid for S. meliloti osmoadaptation. Indeed, we identified a 200-kb region in pSymB needed for adaptation to saline shock which has a high density of osmoregulated genes.
Figures




References
-
- Becker, A., H. Bergès, E. Krol, C. Bruand, S. Rüberg, D. Capela, E. Lauber, E. Meilhoc, F. Ampe, F. J. de Bruijn, J. Fourment, A. Francez-Charlot, D. Kahn, H. Küster, C. Liebe, A. Pühler, S. Weidner, and J. Batut. 2004. Global changes in gene expression in Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 under microoxic and symbiotic conditions. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 17:292-303. - PubMed
-
- Beringer, J. E. 1974. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J. Gen. Microbiol. 84:188-198. - PubMed
-
- Bohin, J.-P. 2000. Osmoregulated periplasmic glucans in proteobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 186:11-19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

