Structure and organization of interstitial cells of Cajal in the gastrointestinal tract
- PMID: 16916909
- PMCID: PMC1890414
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116624
Structure and organization of interstitial cells of Cajal in the gastrointestinal tract
Abstract
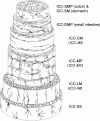
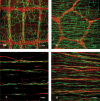
The morphological features of interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract are described based on observations of laboratory animals including mice, rats and guinea-pigs, using immunohistochemical staining for Kit and electron microscopy. ICC show a specific distribution, arrangement and cell shape depending on their location within various regions and tissue layers of the GI tract. Hence they are classified into several subtypes. The stomach shows distinct regional variations in the distribution of subtypes of ICC from the cardia to pylorus, whereas the small intestine and colon both seem to retain nearly the same distribution pattern of subtypes of ICC throughout each organ. All subtypes of ICC share common ultrastructural features, such as the presence of numerous mitochondria, abundant intermediate filaments, and formation of gap junctions with the same type of cells and with smooth muscle cells. In addition, depending on their species and anatomical location, some subtypes of ICC show some features typical of smooth muscle cells including a basal lamina, caveolae, subsurface cisterns and dense bodies. ICC are somewhat heterogeneous morphologically. A question is raised on a special relationship between their ultrastructural features and dependency on Kit/stem cell factor system. As the neuromediator function of ICC, reciprocal distribution of ICC and gap junctions in the muscle coat is demonstrated by the comparison of Kit immunoreactive cells and gap junction protein connexin 43 in both small intestine and colon.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative morphology of interstitial cells of Cajal: ultrastructural characterization.Microsc Res Tech. 1999 Nov 15;47(4):267-85. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(19991115)47:4<267::AID-JEMT5>3.0.CO;2-O. Microsc Res Tech. 1999. PMID: 10602287 Review.
-
Enteric motor neurons form synaptic-like junctions with interstitial cells of Cajal in the canine gastric antrum.Cell Tissue Res. 2003 Mar;311(3):299-313. doi: 10.1007/s00441-002-0657-1. Epub 2003 Feb 25. Cell Tissue Res. 2003. PMID: 12658438
-
Distribution of interstitial cells of Cajal and gap junction protein, Cx 43 in the stomach of wild-type and W/Wv mutant mice.Anat Embryol (Berl). 2002 Dec;206(1-2):57-65. doi: 10.1007/s00429-002-0279-0. Epub 2002 Nov 9. Anat Embryol (Berl). 2002. PMID: 12478368
-
Ultrastructural characterization of interstitial cells of Cajal associated with the submucosal plexus in the proximal colon of the guinea pig.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Feb;347(2):319-26. doi: 10.1007/s00441-011-1312-5. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 22290633
-
Intercellular coupling of interstitial cells of cajal in the digestive tract.Int Rev Cytol. 2005;242:249-82. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(04)42006-3. Int Rev Cytol. 2005. PMID: 15598471 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrical events underlying organized myogenic contractions of the guinea pig stomach.J Physiol. 2006 Nov 1;576(Pt 3):659-65. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116491. Epub 2006 Jul 27. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16873400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ca2+ dynamics in interstitial cells: foundational mechanisms for the motor patterns in the gastrointestinal tract.Physiol Rev. 2024 Jan 1;104(1):329-398. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00036.2022. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37561138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ca2+ signalling behaviours of intramuscular interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine colon.J Physiol. 2019 Jul;597(14):3587-3617. doi: 10.1113/JP278036. Epub 2019 Jun 13. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31124144 Free PMC article.
-
CrossTalk opposing view: Interstitial cells are not involved and physiologically important in neuromuscular transmission in the gut.J Physiol. 2016 Mar 15;594(6):1511-3. doi: 10.1113/JP271587. Epub 2016 Feb 3. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26842563 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The importance of interstitial cells of cajal in the gastrointestinal tract.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jan-Feb;19(1):3-15. doi: 10.4103/1319-3767.105909. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23319032 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beckett EAH, Takeda Y, Yanase H, Sanders KM, Ward SM. Synaptic specializations exist between enteric motor nerves and interstitial cells of Cajal in the murine stomach. J Comp Neurol. 2005;493:193–206. - PubMed
-
- Berezin I, Huizinga JD, Daniel EE. Interstitial cells of Cajal in the canine colon: a special communication network at the inner border of the circular muscle. J Comp Neurol. 1988;373:42–51. - PubMed
-
- Burns AJ, Herbert TM, Ward SM, Sanders KM. Interstitial cells of Cajal in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract as revealed by c-Kit immunohistochemistry. Cell Tissue Res. 1997;290:11–20. - PubMed
-
- Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Cortesini C. Ultrastructural features and localization of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the smooth muscle coat of human esophagus. J Submicrosc Cytol Patol. 1985;17:187–197. - PubMed
-
- Gabella G. Innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;59:129–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

