Ca2+ signalling in urethral interstitial cells of Cajal
- PMID: 16916912
- PMCID: PMC1890406
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.115956
Ca2+ signalling in urethral interstitial cells of Cajal
Abstract
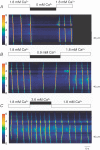
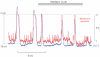
Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) in the urethra have been proposed as specialized pacemakers that are involved in the generation of urethral tone and therefore the maintenance of urinary continence. Recent studies on freshly dispersed ICC from the urethra of rabbits have demonstrated that pacemaker activity in urethra ICC is characterized by spontaneous transient depolarizations (STDs) under current clamp and spontaneous transient inward currents (STICs) under voltage clamp. When these events were simultaneously recorded with changes in intracellular Ca(2+) (using a Nipkow spinning disk confocal microscope) they were found to be associated with global Ca(2+) oscillations. In this short review we will consider some of these recent findings regarding the contribution of intracellular Ca(2+) stores and Ca(2+) influx to the generation of pacemaker activity in urethral ICC with particular emphasis on the contribution of reverse Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange (NCX).
Figures
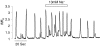
Similar articles
-
Contribution of reverse Na+-Ca2+ exchange to spontaneous activity in interstitial cells of Cajal in the rabbit urethra.J Physiol. 2006 Aug 1;574(Pt 3):651-61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.110932. Epub 2006 May 25. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16728449 Free PMC article.
-
Interstitial cells of Cajal in the urethra.J Cell Mol Med. 2006 Apr-Jun;10(2):280-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2006.tb00399.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16796799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of mitochondria in modulation of spontaneous Ca2+ waves in freshly dispersed interstitial cells of Cajal from the rabbit urethra.J Physiol. 2008 Oct 1;586(19):4631-42. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.159194. Epub 2008 Aug 14. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18703577 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Ca(2+) influx in spontaneous Ca(2+) wave propagation in interstitial cells of Cajal from the rabbit urethra.J Physiol. 2015 Aug 1;593(15):3333-50. doi: 10.1113/JP270883. Epub 2015 Jun 26. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26046824 Free PMC article.
-
Organization and function of ICC in the urinary tract.J Physiol. 2006 Nov 1;576(Pt 3):689-94. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116657. Epub 2006 Aug 17. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16916908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of high [K(+)]o on spontaneous Ca(2+) waves in freshly isolated interstitial cells of Cajal from the rabbit urethra.Physiol Rep. 2014 Jan 21;2(1):e00203. doi: 10.1002/phy2.203. eCollection 2014 Jan 1. Physiol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24744882 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+ imaging of activity in ICC-MY during local mucosal reflexes and the colonic migrating motor complex in the murine large intestine.J Physiol. 2010 Nov 15;588(Pt 22):4453-74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.196824. Epub 2010 Sep 27. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20876203 Free PMC article.
-
Smooth muscle cell calcium activation mechanisms.J Physiol. 2008 Nov 1;586(21):5047-61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.160440. Epub 2008 Sep 11. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18787034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Properties of spontaneous Ca2+ transients recorded from interstitial cells of Cajal-like cells of the rabbit urethra in situ.J Physiol. 2007 Sep 1;583(Pt 2):505-19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.136697. Epub 2007 Jul 5. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17615099 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of interstitial cells of Cajal in the control of smooth muscle excitability. Proceedings of a symposium. July 22, 2006. Okayama, Japan.J Physiol. 2006 Nov 1;576(Pt 3):651-721. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.121178. Epub 2006 Sep 21. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16990407 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Blaustein MP, Lederer WJ. Sodium/calcium exchange: its physiological implications. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:763–854. Review. - PubMed
-
- Bradley E, Hollywood MA, McHale NG, Thornbury KD, Sergeant GP. Pacemaker activity in urethral interstitial cells is not dependent on capacitative calcium entry. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;289:C625–C632. - PubMed
-
- Gordienko DV, Zholos AV, Bolton TB. Membrane ion channels as physiological targets for local Ca2+ signalling. J Microsc. 1999;196:305–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

