Molecular basis for the herbicide resistance of Roundup Ready crops
- PMID: 16916934
- PMCID: PMC1559744
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0603638103
Molecular basis for the herbicide resistance of Roundup Ready crops
Abstract
The engineering of transgenic crops resistant to the broad-spectrum herbicide glyphosate has greatly improved agricultural efficiency worldwide. Glyphosate-based herbicides, such as Roundup, target the shikimate pathway enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase, the functionality of which is absolutely required for the survival of plants. Roundup Ready plants carry the gene coding for a glyphosate-insensitive form of this enzyme, obtained from Agrobacterium sp. strain CP4. Once incorporated into the plant genome, the gene product, CP4 EPSP synthase, confers crop resistance to glyphosate. Although widely used, the molecular basis for this glyphosate-resistance has remained obscure. We generated a synthetic gene coding for CP4 EPSP synthase and characterized the enzyme using kinetics and crystallography. The CP4 enzyme has unexpected kinetic and structural properties that render it unique among the known EPSP synthases. Glyphosate binds to the CP4 EPSP synthase in a condensed, noninhibitory conformation. Glyphosate sensitivity can be restored through a single-site mutation in the active site (Ala-100-Gly), allowing glyphosate to bind in its extended, inhibitory conformation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: No conflicts declared.
Figures
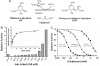

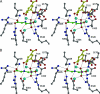
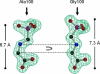
 N bond next to the carboxyl group.
N bond next to the carboxyl group.References
-
- Barry G. F., Kishore G. M., Padgette S. R., Stallings W. C. U.S. Patent. 5633435. 1997.
-
- Padgette S. R., Kolacz K. H., Delannay X., Re D. B., LaVallee B. J., Tinius C. N., Rhodes W. K., Otero Y. I., Barry G. F., Eichholz D. A., et al. Crop Sci. 1995;35:1451–1461.
-
- Johanns M., Wiyatt S. D., editors. National Agriculture Statistics Service. Acreage. Washington, DC: U.S. Dept. of Agriculture; 2005. Jun 30,
-
- Comai L., Sen L. C., Stalker D. M. Science. 1983;221:370–371. - PubMed
-
- Padgette S. R., Re D. B., Gasser C. S., Eichholtz D. A., Frazier R. B., Hironaka C. M., Levine E. B., Shah D. M., Fraley R. T., Kishore G. M. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:22364–22369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

