Surfactant dysfunction in SP-A-/- and iNOS-/- mice with mycoplasma infection
- PMID: 16917077
- PMCID: PMC1899299
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0049OC
Surfactant dysfunction in SP-A-/- and iNOS-/- mice with mycoplasma infection
Abstract
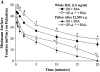
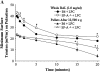
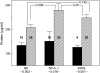
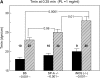
Surfactant dysfunction was studied in C57BL/6 (B6), B6.SP-A(-/-), and B6.iNOS(-/-) mice with pulmonary mycoplasma infection (10(7) colony-forming units). Cell-free bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) from uninfected B6.SP-A(-/-) versus B6 mice had a reduced content of very large aggregates (VLA) and an increase in intermediate large aggregates (ILA), with no difference in total large aggregates (LA = VLA + ILA). However, LA from uninfected B6.SP-A(-/-) versus B6 mice contained less protein and were more sensitive to inhibition by serum albumin and lysophosphatidylcholine in pulsating bubble studies in vitro. Infection with Mycoplasma pulmonis caused significant lung injury and surfactant abnormalities in B6.SP-A(-/-), B6.iNOS(-/-), and B6 mice at 24, 48, 72 h after infection compared with uninfected mice of the same strain. Analyses of time-pooled data indicated that mycoplasma-infected B6.SP-A(-/-) and B6.iNOS(-/-) mice had significantly lower levels of LA and higher protein/phospholipid ratios in BAL compared with infected B6 mice. Infected B6.iNOS(-/-) versus B6 mice also had increased minimum surface tensions on the pulsating bubble and decreased levels of surfactant protein (SP)-B in BAL. These results indicate that pulmonary mycoplasma infection in vivo causes lung injury and surfactant abnormalities that are dependent in part on iNOS and SP-A. In addition, SP-A deficiency modifies surfactant aggregate content and lowers the inhibition resistance of LA surfactant in vitro compared with congenic normal mice.
Figures










References
-
- Cassell GH, Gray GC, Waites KB. Mycoplasma infections. In Fauci AS, Braunwald E, Isselbacher KJ, Martin JB, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, editors. Harrison's principles of internal medicine, 14th ed. New York: McGraw Hill Companies, Inc.; 1998. pp. 1052–1055.
-
- Hickman-Davis JM, Lindsey JR, Zhu S, Matalon S. Surfactant protein A mediates mycoplasmacidal activity of alveolar macrophages. Am J Physiol 1998;274:L270–L277. - PubMed
-
- Daniels CB, Orgeig S. Pulmonary surfactant: the key to the evolution of air breathing. News Physiol Sci 2003;18:151–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

