Induction of squamous cell carcinoma of forestomach in diabetic rats by single alloxan treatment
- PMID: 16918997
- PMCID: PMC11158268
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00279.x
Induction of squamous cell carcinoma of forestomach in diabetic rats by single alloxan treatment
Abstract
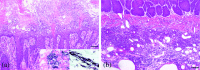
Male rats of WBN/Kob strain are one of the diabetic model animals and develop long-lasting diabetic symptoms and some complications from about 40 weeks of age without any treatment. A single intravenous dose of alloxan, a non-genotoxic diabetogenic chemical, frequently induced proliferative lesions of squamous epithelium in tongue, esophagus and forestomach of male and female WBN/Kob rats, and hastened the onset and acceleration of diabetic conditions. Histopathologically, proliferative changes of squamous cell of forestomach varied with the severity of hyperplasia in alloxan-treated rats (100% of 31 males and 94.1% of 17 females) and progressed to SCC in approximately 20% of all rats. Metastasis to regional lymph nodes was also observed in two cases. Proliferative changes were most severe in the forestomach and were constantly accompanied with chronic suppurative inflammation of the mucosal epithelium with infection of filamentous fungi and/or bacterial colonies. In contrast, forestomach of the spontaneously diabetic male rats showed only slight hyperplasia of the mucosal epithelium confined to the limiting ridge in approximately 30% of the cases. All non-diabetic female rats showed neither proliferative changes nor the inflammatory process in the mucosa. Immunohistochemically, COX-2 and iNOS were positive in these chronic suppurative inflammatory lesions accompanied by proliferative squamous epithelium. From these results, it is suggested that chronic inflammatory processes play an important role in the pathogenesis of alloxan-induced SCC. An experimental system of alloxan-induced SCC might serve as a suitable model for the study of the inflammation-related promotion of carcinogenesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prevention of proliferative changes of forestomach mucosa by blood glucose control with insulin in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Cancer Sci. 2009 Apr;100(4):595-600. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.01081.x. Epub 2009 Jan 18. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19154414 Free PMC article.
-
A novel diabetic murine model of Candida albicans-induced mucosal inflammation and proliferation.J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:509325. doi: 10.1155/2014/509325. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Diabetes Res. 2014. PMID: 24693542 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the antifungal agent itraconazole on proliferative changes of the forestomach mucosa in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Toxicol Pathol. 2009 Oct;37(6):790-8. doi: 10.1177/0192623309344204. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Toxicol Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19700660
-
Antimicrobial agent, tetracycline, enhanced upper alimentary tract Candida albicans infection and its related mucosal proliferation in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Toxicol Pathol. 2012 Oct;40(7):1014-9. doi: 10.1177/0192623312447287. Epub 2012 May 18. Toxicol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22609949
-
Evaluation of potential human carcinogenicity of the synthetic monomer ethyl acrylate.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;53(1):6-15. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2008.09.005. Epub 2008 Oct 5. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18930102 Review.
Cited by
-
Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Dorsum of the Tongue Following Chronic Hypertrophic Candidiasis: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2025 Apr 24;17(4):e82951. doi: 10.7759/cureus.82951. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40416125 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of proliferative changes of forestomach mucosa by blood glucose control with insulin in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Cancer Sci. 2009 Apr;100(4):595-600. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.01081.x. Epub 2009 Jan 18. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19154414 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced tumorigenesis of forestomach tumors induced by N-Methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in rats with hypoinsulinemic diabetes.Cancer Sci. 2010 Jul;101(7):1604-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01589.x. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20497417 Free PMC article.
-
A novel diabetic murine model of Candida albicans-induced mucosal inflammation and proliferation.J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:509325. doi: 10.1155/2014/509325. Epub 2014 Feb 18. J Diabetes Res. 2014. PMID: 24693542 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of Correlation between Aberrant p16, RAR-β2, TIMP3, ERCC1, and BRCA1 Protein Expression and Promoter Methylation in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Accompanying Candida albicans-Induced Inflammation.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 13;11(7):e0159090. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159090. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27410681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsuchitani M, Saegusa T, Narama I et al. A new diabetic strain of rat (WBN/Kob). Lab Anim 1985; 19: 200–7. - PubMed
-
- Nakama K, Shichinohe K, Kobayashi K et al. Spontaneous diabetes‐like syndrome in WBN/KOB rats. Acta Diabetol Lat 1985; 22: 335–42. - PubMed
-
- Narama I, Kino I. Peripheral motor neuropathy in spontaneously diabetic WBN/Kob rats: a morphometric and electron microscopic study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1989; 79: 52–60. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki K, Miura K, Tsuchitani M et al. Peripheral neuropathy in the spontaneously diabetic WBN/Kob rat. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 1996; 92: 603–7. - PubMed
-
- Ishizaki M, Masuda Y, Fukuda Y et al. Renal lesions in a strain of spontaneously diabetic WBN/Kob rats. Acta Diabetol Lat 1987; 24: 27–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

