Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 (BRMS1) is stabilized by the Hsp90 chaperone
- PMID: 16919237
- PMCID: PMC1557677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.08.005
Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 (BRMS1) is stabilized by the Hsp90 chaperone
Abstract
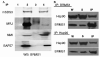
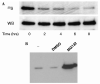
Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 (BRMS1) is a member of the mSin3-HDAC transcription co-repressor complex. However, the proteins associated with BRMS1 have not been fully identified. Yeast two-hybrid screen, immuno-affinity chromatography, and co-immunoprecipitation experiments were performed to identify BRMS1 interacting proteins (BIPs). In addition to known core mSin3 transcriptional complex components RBBP1 and mSDS3, BRMS1 interacted with other proteins including three chaperones: DNAJB6 (MRJ), Hsp90, and Hsp70. Hsp90 is a known target of HDAC6 and reversible acetylation is one of the mechanisms that is implicated in regulation of Hsp90 chaperone complex activity. BRMS1 interacted with class II HDACs, HDAC 4, 5, and 6. We further found that BRMS1 is stabilized by Hsp90, and its turnover is proteasome dependent. The stability of BRMS1 protein may be important in maintaining the functional role of BRMS1 in metastasis suppression.
Figures



References
-
- Kang YB, Siegel PM, Shu WP, Drobnjak M, Kakonen SM, Cordón-Cardo C, Guise TA, Massagué J. A multigenic program mediating breast cancer metastasis to bone. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:537–549. - PubMed
-
- Debies MT, Welch DR. Genetic basis of human breast cancer metastasis. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia. 2001;6:441–451. - PubMed
-
- Seraj MJ, Samant RS, Verderame MF, Welch DR. Functional evidence for a novel human breast carcinoma metastasis suppressor, BRMS1, encoded at chromosome 11q13. Cancer Res. 2000;60:2764–2769. - PubMed
-
- Samant RS, Seraj MJ, Saunders MM, Sakamaki T, Shevde LA, Harms JF, Leonard TO, Goldberg SF, Budgeon LR, Meehan WJ, Winter CR, Christensen ND, Verderame MF, Donahue HJ, Welch DR. Analysis of mechanisms underlying BRMS1 suppression of metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 2001;18:683–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

