Anatomical profiling of nuclear receptor expression reveals a hierarchical transcriptional network
- PMID: 16923397
- PMCID: PMC6211849
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.049
Anatomical profiling of nuclear receptor expression reveals a hierarchical transcriptional network
Abstract
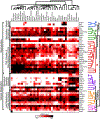
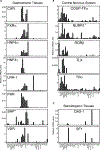
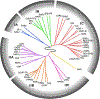
In multicellular organisms, the ability to regulate reproduction, development, and nutrient utilization coincided with the evolution of nuclear receptors (NRs), transcription factors that utilize lipophilic ligands to mediate their function. Studying the expression profile of NRs offers a simple, powerful way to obtain highly relational information about their physiologic functions as individual proteins and as a superfamily. We surveyed the expression of all 49 mouse NR mRNAs in 39 tissues, representing diverse anatomical systems. The resulting data set uncovers several NR clades whose patterns of expression indicate their ability to coordinate the transcriptional programs necessary to affect distinct physiologic pathways. Remarkably, this regulatory network divides along the following two physiologic paradigms: (1) reproduction, development, and growth and (2) nutrient uptake, metabolism, and excretion. These data reveal a hierarchical transcriptional circuitry that extends beyond individual tissues to form a meganetwork governing physiology on an organismal scale.
Figures
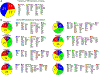
References
-
- Akhmedov NB, Piriev NI, Chang B, Rapoport AL, Hawes NL, Nishina PM, Nusinowitz S, Heckenlively JR, Roderick TH, Kozak CA, et al. (2000). A deletion in a photoreceptor-specific nuclear receptor mRNA causes retinal degeneration in the rd7 mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 5551–5556. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barish GD, Downes M, Alaynick WA, Yu RT, Ocampo CB, Bookout AL, Mangelsdorf DJ, and Evans RM (2005). A Nuclear Receptor Atlas: macrophage activation. Mol. Endocrinol 19, 2466–2477. - PubMed
-
- Beland M, and Lohnes D (2005). Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factor members repress retinoic acid-induced Cdx1 expression. J. Biol. Chem 280, 13858–13862. - PubMed
-
- Beuschlein F, Keegan CE, Bavers DL, Mutch C, Hutz JE, Shah S, Ulrich-Lai YM, Engeland WC, Jeffs B, Jameson JL, and Hammer GD (2002). SF-1, DAX-1, and acd: molecular determinants of adrenocortical growth and steroidogenesis. Endocr. Res 28, 597–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

