Life with a single isoform of Akt: mice lacking Akt2 and Akt3 are viable but display impaired glucose homeostasis and growth deficiencies
- PMID: 16923958
- PMCID: PMC1636753
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00722-06
Life with a single isoform of Akt: mice lacking Akt2 and Akt3 are viable but display impaired glucose homeostasis and growth deficiencies
Abstract
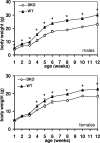
To address the issues of isoform redundancy and isoform specificity of the Akt family of protein kinases in vivo, we generated mice deficient in both Akt2 and Akt3. In these mice, only the Akt1 isoform remains to perform essential Akt functions, such as glucose homeostasis, proliferation, differentiation, and early development. Surprisingly, we found that Akt2(-/-) Akt3(-/-) and even Akt1(+/-) Akt2(-/-) Akt3(-/-) mice developed normally and survived with minimal dysfunctions, despite a dramatic reduction of total Akt levels in all tissues. A single functional allele of Akt1 appears to be sufficient for successful embryonic development and postnatal survival. This is in sharp contrast to the previously described lethal phenotypes of Akt1(-/-) Akt2(-/-) mice and Akt1(-/-) Akt3(-/-) mice. However, Akt2(-/-) Akt3(-/-) mice were glucose and insulin intolerant and exhibited an approximately 25% reduction in body weight compared to wild-type mice. In addition, we found substantial reductions in relative size and weight of the brain and testis in Akt2(-/-) Akt3(-/-) mice, demonstrating an in vivo role for both Akt2 and Akt3 in the determination of whole animal size and individual organ sizes.
Figures
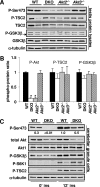

 , P < 0.05). In all four graphs, differences in Akt2−/− Akt3−/− versus Akt2−/− mice were not significant. (C) Active Akt and GSK3β in insulin-responsive tissues of wild-type and Akt2−/− Akt3−/− mice after in vivo insulin stimulation. Three-month-old male mice were made to fast overnight and injected with either saline (−) or insulin (10 mU/g body weight). After 12 min, the indicated tissues were harvested. Lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Samples are from individual mice (n = 3 for saline controls; n = 4 for insulin stimulation).
, P < 0.05). In all four graphs, differences in Akt2−/− Akt3−/− versus Akt2−/− mice were not significant. (C) Active Akt and GSK3β in insulin-responsive tissues of wild-type and Akt2−/− Akt3−/− mice after in vivo insulin stimulation. Three-month-old male mice were made to fast overnight and injected with either saline (−) or insulin (10 mU/g body weight). After 12 min, the indicated tissues were harvested. Lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Samples are from individual mice (n = 3 for saline controls; n = 4 for insulin stimulation).References
-
- Bae, S. S., H. Cho, J. Mu, and M. J. Birnbaum. 2003. Isoform-specific regulation of insulin-dependent glucose uptake by Akt/protein kinase B. J. Biol. Chem. 278:49530-49536. - PubMed
-
- Baker, J., J. P. Liu, E. J. Robertson, and A. Efstratiadis. 1993. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell 75:73-82. - PubMed
-
- Brazil, D. P., Z. Z. Yang, and B. A. Hemmings. 2004. Advances in protein kinase B signalling: AKTion on multiple fronts. Trends Biochem. Sci. 29:233-242. - PubMed
-
- Chang, P. Y., Y. Le Marchand-Brustel, L. A. Cheatham, and D. E. Moller. 1995. Insulin stimulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase, p90rsk, and p70 S6 kinase in skeletal muscle of normal and insulin-resistant mice. Implications for the regulation of glycogen synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 270:29928-29935. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
